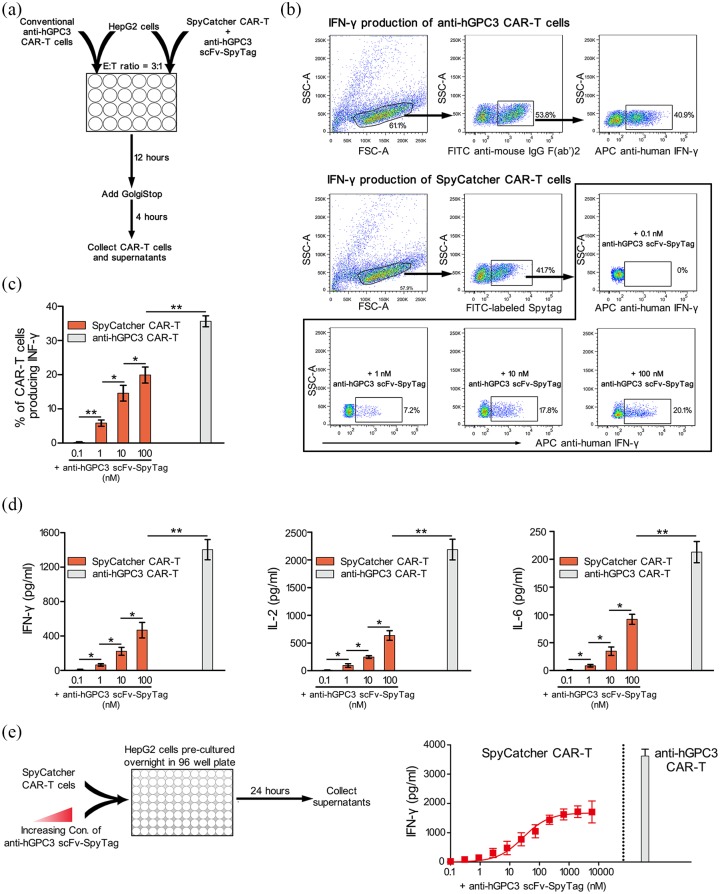
Figure 5.
Split anti-hGPC3 CAR-T cells significantly reduce cytokine release compared with conventional CAR-T cells. (a) Schematic diagram of the experimental process. CAR-T cells generated from healthy donors (n = 3) were cocultured with HepG2 cells in 24-well plates at a 3:1 E:T ratio for 16 h; GolgiStop was added for the last 4 h to block release of cytokines. CAR-T cells were collected and analyzed by intracellular staining. Supernatants were also collected and cytokines were measured by ELISA. For each donor, the experiment was repeated twice. (b) Representative dot plots showing the gating strategy and the IFN-γ+ CAR-T cells. (c) The proportion of IFN-γ-producing CAR-T cells. Data were pooled and plotted as mean ± SD. (d) The concentrations of cytokines in the coculture supernatants were measured by ELISA. Data were pooled and plotted as mean ± SD. All comparisons were analyzed by two-tailed Student’s t test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. (e) Spycatcher CAR-T cells (with the addition of a serial diluted anti-hGPC3 scFv- SpyTag) and conventional anti-hGPC3 CAR-T cells were cocultured with HepG2 cells in 96-well plates at a 3:1 E:T ratio for 24 h (left). Cytokines in the supernatants were measured by ELISA. Data of IFN-γ concentration in different groups were pooled and plotted as mean ± SD.
CAR-T, chimeric antigen receptor T; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; E:T, effector:target; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; hGPC3, human glypican-3; IFN, interferon; SD, standard deviation.