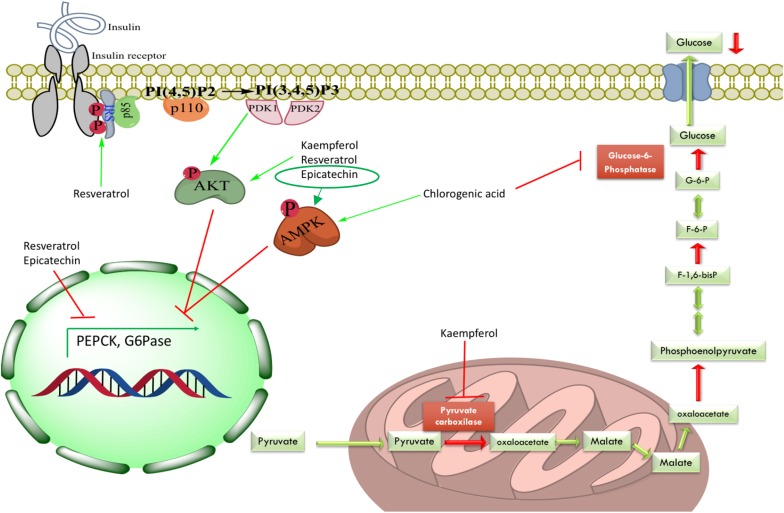
FIGURE 3.
Mechanisms of hepatic gluconeogenesis inhibition exerted by some identified compounds from evaluated plant extracts in this study. Active compounds could have two main ways to decrease HGO: (1) direct inhibition of gluconeogenic enzymes, for instance, inhibition of G6Pase system by CA and inhibition of PC by kaempferol; or (2) decreasing expression levels of gluconeogenic enzymes via Akt pathway (kaempferol, resveratrol and, epicatechin) or AMPK activation (CA and epicatechin). IRS, insulin receptor substrate; PI(4,5)P2, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; PI(3,4,5)P3, phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-triphosphate; PDK1, phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1; PDK2, phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 2; Akt, protein kinase B; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; G6P, glucose-6-phosphate; F-6-P, fructose-6-phosphate; F-1,6-bisP, fructose-1,6-bisphosphate; G6Pase, glucose-6-phosphatase.