Fig. 3 |. The cell cycle during dissolution of pluripotency and cell differentiation.
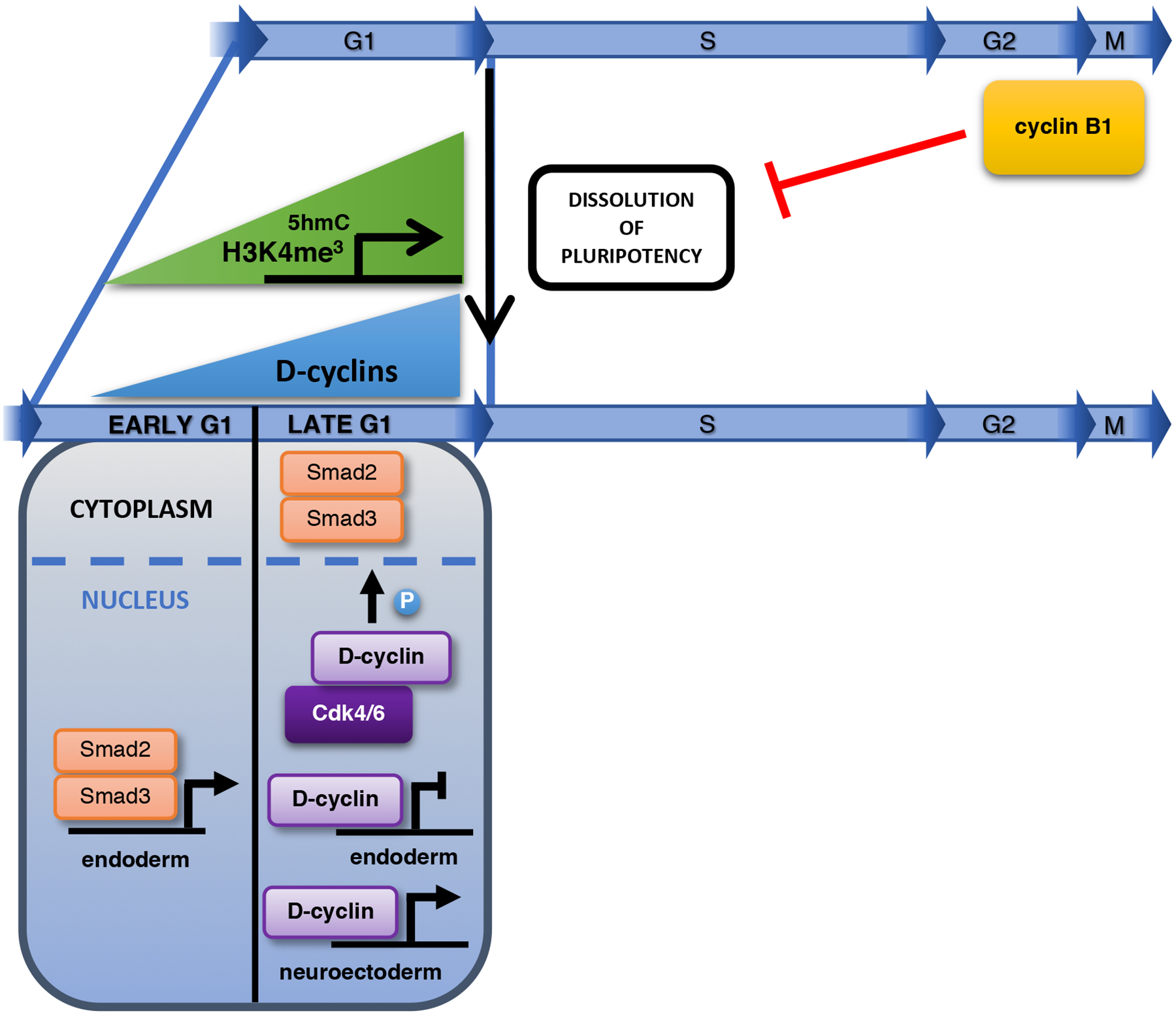
G1 phase may provide a window of opportunity for the dissolution of pluripotency, as during this phase many developmental genes contain permissive epigenetic marks (H3K4me3 and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine). Cyclin B1 actively prevents pluripotency exit. Increased expression of D cyclins in late G1 triggers the phosphorylation and cytoplasmic retention of Smad2/3, thereby inhibiting endodermal differentiation. In addition, D cyclins directly repress the expression of endodermal genes and augment the expression of neuroectodermal genes. Abbreviations: 5hmC: 5-hydroxymethylcytosine.
