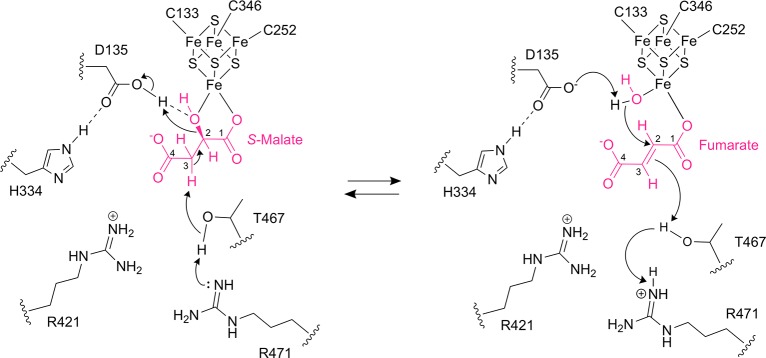
Figure 6.
Proposed catalytic mechanism for class I FHs. In the dehydration of S-malate to fumarate, first, a proton is abstracted from S-malate C3 by T467 that is activated by either of the two arginine residues (R421 and R471), which accept the proton. In the second step, D135 donates a proton to the S-malate C2-hydroxyl group for elimination as water and subsequent formation of fumarate. The negative charge of D135 is stabilized by H334. In the hydration of fumarate to S-malate, D135 abstracts a proton from the water molecule bound to the [4Fe-4S] cluster to form a hydroxyl group for addition to C2 of fumarate, and then T467 and either of its partners R421 and R471 donate a proton to C3 of fumarate for subsequent formation of S-malate. The [4Fe-4S] cluster acts as a Lewis acid to activate the hydroxyl group from S-malate for elimination or water for addition.