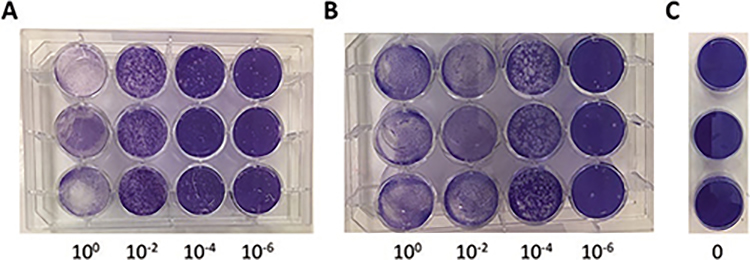
Fig. 2.
Plaque assay of ZIKV-infected Vero cells. Vero cells were plated in a 12-well plate and left to attach overnight. The following day, serial dilutions of virus were prepared (10−2, 10−4, 10−6) and 250 μl added to the monolayer of Vero cells (a, b). The increased number of plaques seen in b compared to a, indicates a higher viral titer. As a control, media without virus was added to Vero (c). After 2-h adsorption, agarose overlay medium was added and let to solidify. The plates were then incubated at 37 °C for about 3–4 days. The overlay was then removed, and the cells were stained with 1% crystal violet for about 20 min. The number of plaques was then counted after gently washing off the excess stain. The total number of plaque-forming units (PFU) was determined by dividing the average number of plaques by the dilution factor times the volume added. For example, if there were an average of 20 plaques in the 10−6 wells, the virus titer would be: 20/10−6 * 0.25 ml = 8 * 1 07 PFU/ml