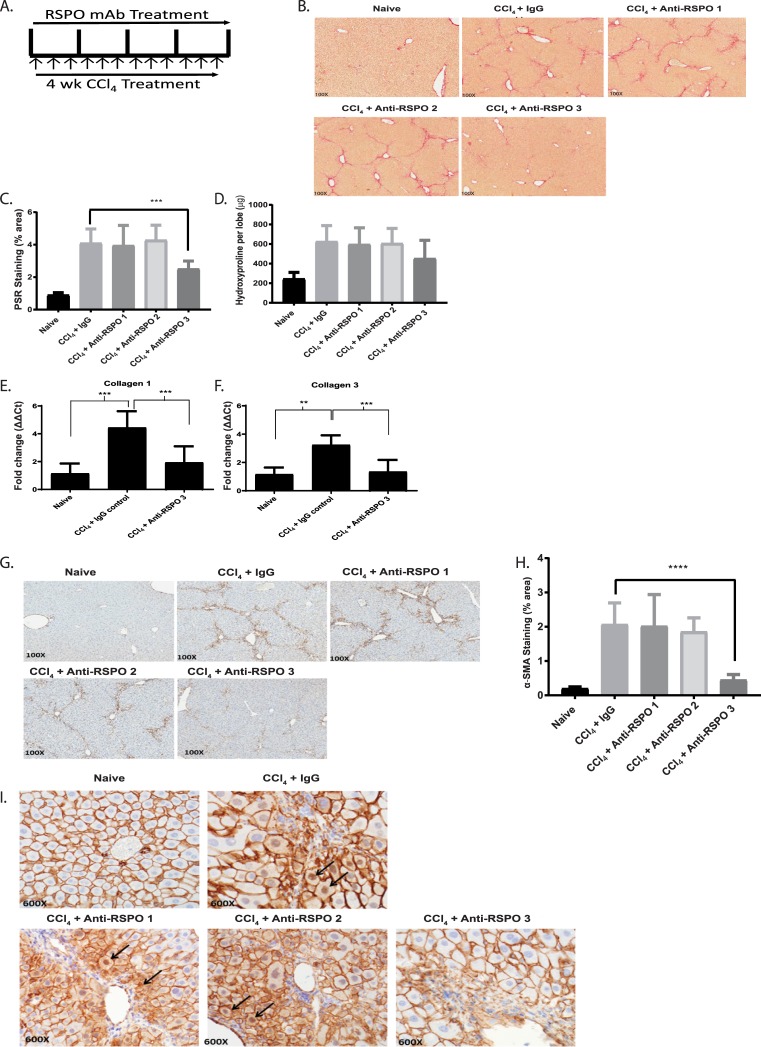
Fig 2. RSPO3 plays an important role in liver fibrosis through activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
A, Treatment scheme of anti-RSPO antibodies in CCl4 liver fibrosis model. B, Representative Picro Sirius Red staining of normal and CCl4 induced mouse livers treated with anti-RSPO1, anti-RSPO2, and OMP-131R10. C, Quantification of Picro Sirius Red staining area. D, Quantification of liver collagen content. E, RT-PCR of collagen I. F, RT-PCR of collagen III. G, Representative immunohistochemistry analysis of α-SMA in the livers of normal and CCl4 induced mouse livers treated with anti-RSPO1, anti-RSPO2 and OMP-131R10. H, Quantification of α-SMA staining area. I, Immunohistochemistry analysis of β-catenin. Nuclear β-catenin were detected in hepatocytes (arrow) in active fibrotic areas. Liver fibrosis was induced by CCl4 injection three times weekly for 4 weeks The mice were treated from day 1 with anti-RSPO1, anti RSPO2 or anti- RSPO3 (OMP-131R10) antibodies at 25 mg/kg once a week (n = 10 animals per group except mineral oil control n = 7). At week 4, the study was terminated and liver levels of hydroxyproline were measured by biochemical methods and percent Picro Sirius Red (PSR), and then quantitated via histological methods. Data is shown as mean ± SEM and % inhibition calculated when compared to the vehicle group following subtraction of the mineral oil control. Statistical comparison was done using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test using the Isotype as a control. *** = p < 0.001; **** = p < 0.0001.