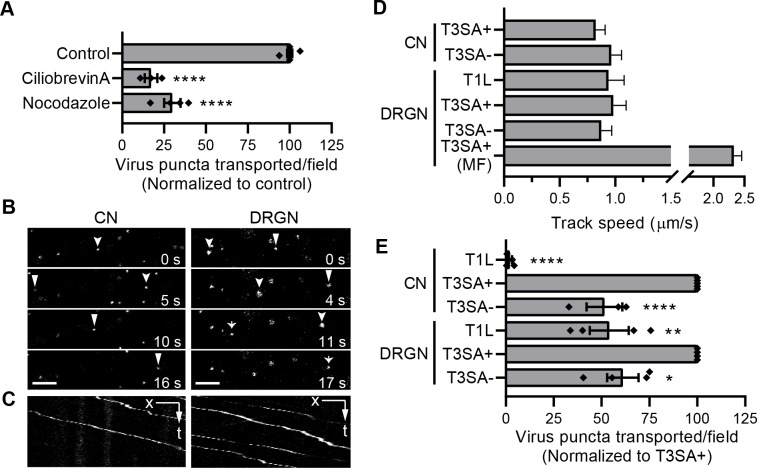
Fig 3. Reovirus undergoes microtubule-dependent fast axonal transport in neurons.
(A) CNs were treated with the drugs shown, adsorbed with T3SA+ virions, and viral puncta transported per field-of-view were enumerated following treatment. Bars indicate mean values from at least two independent experiments, each with one to two samples, normalized to untreated control. Error bars indicate SEM. Individual data points are averages from 8 to 12 fields-of-view from each sample. Values that differ significantly from control by ANOVA and Dunnett's test are indicated (****, P < 0.0001). (B-E) CNs or DRGs were adsorbed with fluorescently-labeled T1L, T3SA+, or T3SA- virions for 30 min. The inoculum was removed, and the motion of virions was recorded using live-cell fluorescence imaging. (B) Time-lapse images of representative fields are shown for T3SA+ with positions of individual puncta tracked over time with discrete arrows or arrowheads. (C) Kymographs corresponding to B show the positions (x) of individual puncta along an axon over time (t). Scale bars, 5 μm. (D) Track speed was calculated for the reovirus strains shown as the overall distance traveled by each fluorescent reovirus puncta during the tracked interval (n > 300 tracks). MF refers to neurons cultured in microfluidic devices. Bars indicate medians, and error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals. (E) Fluorescent puncta transported for distances greater than 5 μm in each 82 x 82 μm field-of-view during 1 min of live-cell imaging were enumerated. Bars indicate means normalized to T3SA+, and error bars indicate SEM. Individual data points are averages from 8 to 12 fields-of-view for each sample. Values that differ significantly from T3SA+ by ANOVA and Dunnett's test are indicated (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.0001).