Fig. 4. YART- and YGT-induced modifications of Rab5.
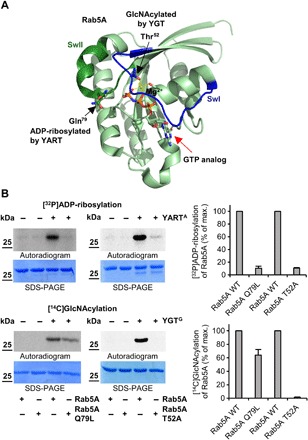
(A) Localization of the sites of Rab5A that are modified by YGT-induced GlcNAcylation and YART-induced ADP-ribosylation. Modification sites are from MS analyses and introduced into the Rab5A structure (PDB ID: 1N6H). Switch-1 (SwI) and switch-2 (SwII) regions are indicated in blue and dark green, respectively. Light green spheres represent the Mg2+ ion, while guanosine triphosphate (GTP) (or a GTP analog) is indicated by red arrow. While YGT modifies Rab5 in Thr52 (black arrow) by GlcNAcylation, YART ADP-ribosylates Gln79 (black arrow). (B) ADP-ribosylation or GlcNAcylation of mutant Rab5 proteins. Wild-type and mutant Q79L or T52A Rab5 proteins (each 2 μg) were incubated with 1 μM YARTA or YGTG, [32P]NAD+, or UDP-[14C]GlcNAc for 1 hour at 21°C. The modifications of proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and phosphorimaging. The amount of modified Rab proteins was normalized to wild-type Rab protein. Means (±SD) of three independent experiments and one representative autoradiogram and Coomassie gel are shown.
