Fig. 5. Functional consequences of Rab5-induced modifications by YART and YGT.
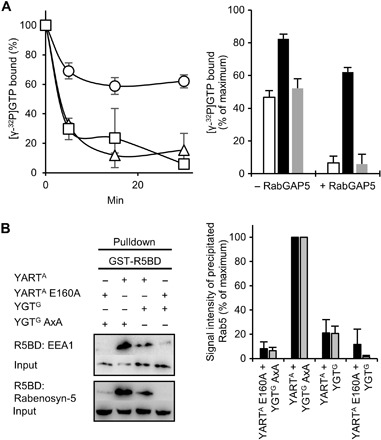
(A) YART effects on GTP hydrolysis by Rab5. Rab5A was ADP-ribosylated by active YARTA or inactive YARTA E160A and loaded with [γ-32P]GTP. Left: RabGAP5-stimulated GTP hydrolysis (time course) by Rab5A pretreated with YARTA (○), with YARTA E160A (□) or untreated control (△). Right: GTP hydrolysis after 30 min with or without RabGAP5 (untreated control, white column; YARTA pretreatment, black column; YARTA E160A pretreatment, gray column). Data are means ± SD (n = 3). (B) Pulldown of Rab5A by the R5BDs of EEA1 and Rabenosyn-5. Rab5A (Flag-tagged) was coexpressed overnight in HeLa cell with active YARTA and YGTG or with the inactive mutants YARTA E160A and YGTG AXA. Cell lysates were incubated with GST-R5BD–coupled beads (30 min). Thereafter, beads were precipitated and washed, and interacting proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blot. Immunoblots with anti-Flag antibody before (input) and after pulldown are shown. Left: One representative experiment. Right: Results of three independent experiments with EEA1 (black column) or with Rabenosyn-5 (gray column) (data are means ± SD). The amount of precipitated Rab5 was normalized to the pulldown of Rab5 after coexpression with YARTA and YGTG AXA.
