Fig. 5. Levels of 2-AG, 2-PG, 2-LG, and 2-OG in intestinal scrapings from the jejunum and plasma levels of GIP, GLP-1, CCK8, and insulin for Rbp2−/− and WT mice 2 hours after oral administration of a challenge of 100 μl of corn oil.
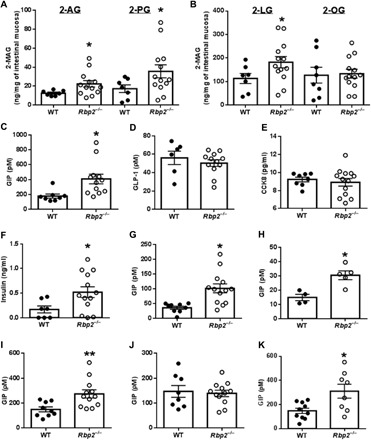
(A and B) Levels of 2-AG, 2-PG, and 2-LG but not 2-OG were significantly elevated in mucosal scrapings obtained from Rbp2−/− mice. (C to F) Plasma levels of GIP (C) and insulin (F) but not GLP-1 (D) or CCK8 (E) were significantly elevated for Rbp2−/− mice receiving the corn oil challenge. (G and H) GIP levels present in plasma of both fed (G) and overnight fasting (H) Rbp2−/− mice were significantly elevated compared to those of matched WT mice. GIP levels were also significantly elevated in younger Rbp2−/− mice fed a high-fat diet for 8 weeks compared to matched WT mice in response to an oral fat challenge (I) but not in response to an oral glucose challenge (J). (K) Blood GIP levels were significantly elevated in Rbp2−/− mice when young (80 to 83 days old) Rbp2−/− and matched WT mice, which had been fed a chow diet throughout life, were challenged with 100 μl of corn oil. All data are presented as means ± SEM. Statistical significance: *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01.
