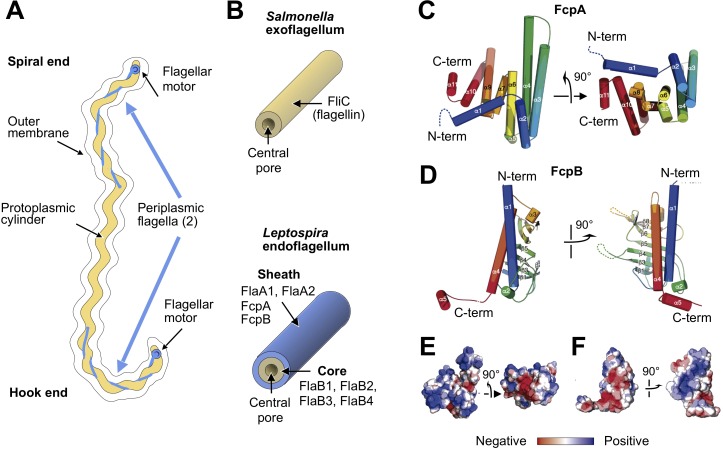
Figure 1. X-ray crystal structures of the sheath proteins, FcpA from L. biflexa and FcpB from L. interrogans.
(A). Schematic of a Leptospira cell. Each cell has two flagella sandwiched between the inner and outer membranes; a single flagellum extends from a motor at either end. (B) Comparison of the predicted endoflagellar filament composition and morphology in Leptospira with the Salmonella exoflagellum. (C) Structure of L. biflexa FcpA in two orthogonal views, depicted as a cartoon colored with a ramp from blue (N-terminus) to red (C-terminus). The dotted line stands for the flexible 54 amino acids at the N-terminus, not visible in electron density. (D) Structure of L. interrogans FcpB in two orthogonal views, similar color code as panel A. (E) Solvent accessible surface of FcpA colored according to an electrostatic potential ramp from negative (red) through neutral (white) to positive (blue) potentials. (F) Solvent accessible surface of FcpB, similar color code as panel E. The perspective was chosen to show the interacting surface of FcpB (positively charged region, panel F left-hand side), in an open-book view (approximately 180° rotated according to a vertical axis), with FcpA (negative cleft, panel E right-hand side). This interaction was later uncovered by studying the whole filament assembly (see Figure 4E).