Figure 3:
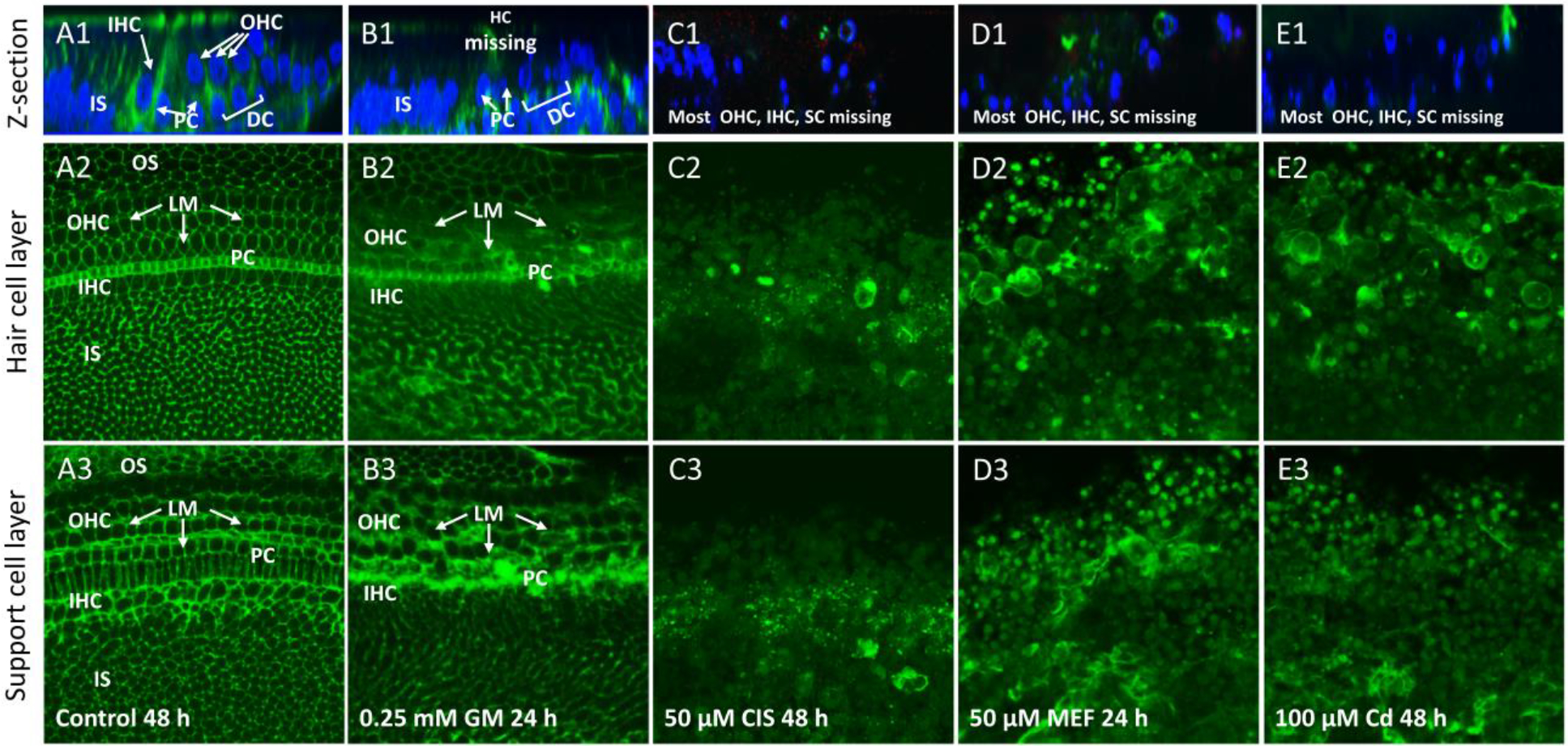
Cochlear organotypic cultures (n ≥6 replicates per condition) from the upper basal turn labeled with an antibody against laminin (LM, green, all rows) and/or with To-Pro-3 (blue, top row only) which labels nuclei. Top row: Representative Z-plane images showing the location of laminin and cell nuclei. Middle row and bottom row only show laminin-labeling of optical sections of surface preparations. Middle row shows sections taken at the level of the hair cells; bottom row shows section from the SC layer. (A1) Z-plane image of control cochlea cultured for 48 h. Strong laminin labeling near and below the surface; nuclear labeling mainly located below the surface in regions occupied by inner hair cells (IHC), outer hair cells (OHC), pillar cells (PC), Deiters cells (DC) and other SC in the inner sulcus (IS) region. (A2) Circumferential rings of LM ln OHC and IHC region and OS region. Strong labeling of laminin in band of PC. Many patches of laminin in IS region. (A3). Circumferential rings of laminin through out the SC layer. (B1–2) Treatment with 0.25 mM GM for 24 h resulted in blurring of circumferential rings of laminin in IHC, OHC and PC regions. (B3) Thickening of circumferential rings of laminin mainly in OHC, IHC and PC regions. (C1–3) Treatment with 50 μM CIS for 48 h reduced the number of cell nuclei; laminin labeling also greatly reduced. (D1–3) Treatment with 50 μM MEF reduced the number of nuclei; laminin labeling in hair cell layer and SC layers reduced and disorganized. (E1–3) Treatment with 100 μM Cd eliminates nuclei; laminin labeling in hair cell and SC layers reduced and greatly disorganized.
