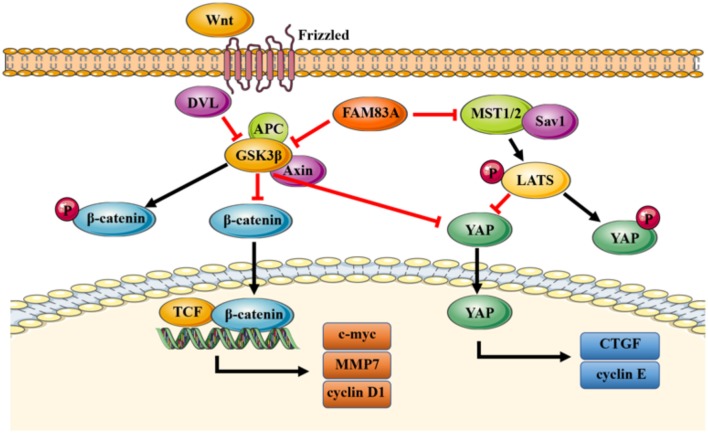
Figure 7.
A proposed model to illustrate the role of FAM83A in the Wnt and Hippo signaling pathways. GSK3β phosphorylates β-catenin and results in the degradation of β-catenin, which inhibits the activity of the Wnt signaling pathway. FAM83A can inhibit GSK3β activity and increase the level of active unphosphorylated β-catenin; active β-catenin then transports into the nucleus and activates the Wnt signaling pathway. Meanwhile, similar to β-catenin, FAM83A may also inhibit the phosphorylation and degradation of YAP, which is induced by the Hippo signaling pathway and enhance the activity of YAP through repressing GSK3β. In addition, FAM83A could downregulate the upstream MST to inhibit the activation of the Hippo signaling pathway. Figures were produced using Servier Medical Art (https://smart.servier.com).