Fig. 6.
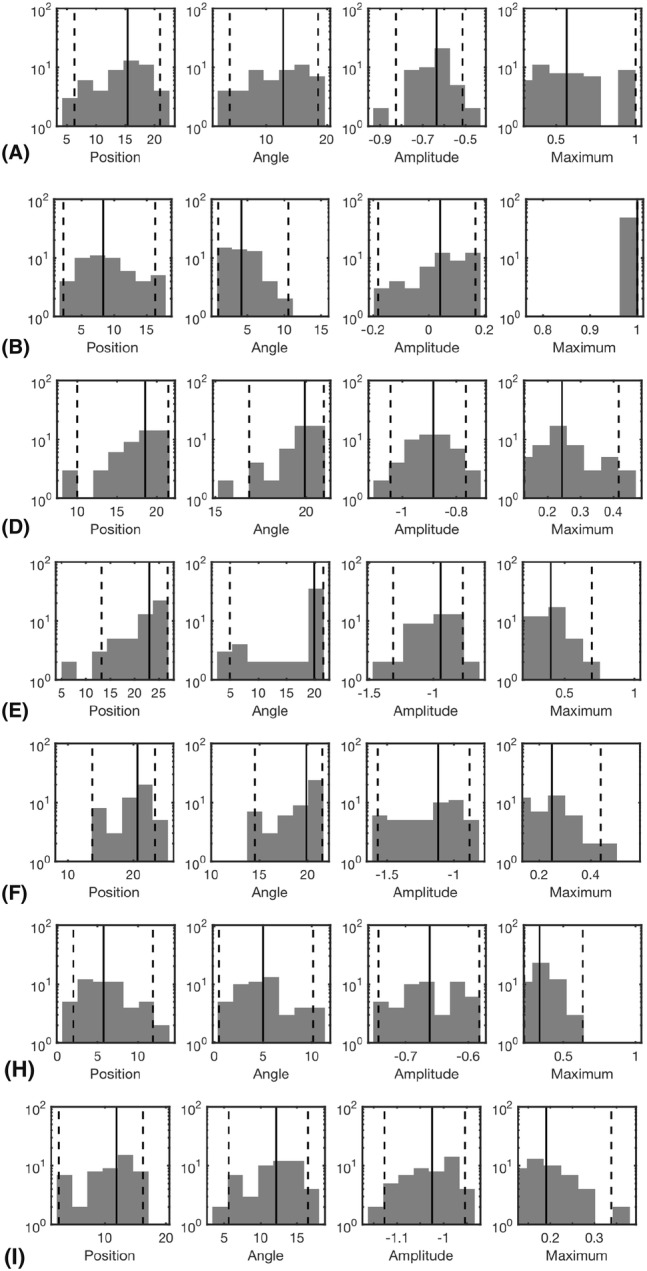
The results of the deep source localization for the numerical experiments (A–I) conducted in the spherical domain (Table 3). The distributions of the position (mm), angle (°) and relative logarithmic (log10) amplitude difference to the exact dipole source, computed in the ROI, have been analyzed as histograms. The sample size is 50. Each reconstruction in the sample has been obtained by reconstructing the activity in the whole brain for an independent random realization of the noise vector and associating the total integrated activity in each ROI to the corresponding (deep or superficial) dipole source. Additionally, the histogram of the relative maximum in the ROI is given. The solid vertical line shows the median for each distribution, and the dashed lines mark the 90% confidence interval. In general, the results show that the IG hyperprior is necessary for detecting the deep source. The accuracy and reliability of the results increase along with the number of multiresolution decompositions. Furthermore, using E/MEG instead of EEG increased the accuracy of the deep source localization, while EEG was advantageous with respect to the amplitude of the deep source. The results are not visualized for the cases in which the localization criterion (relative maximum > 0.05) was satisfied by less than 5% of the reconstructions
