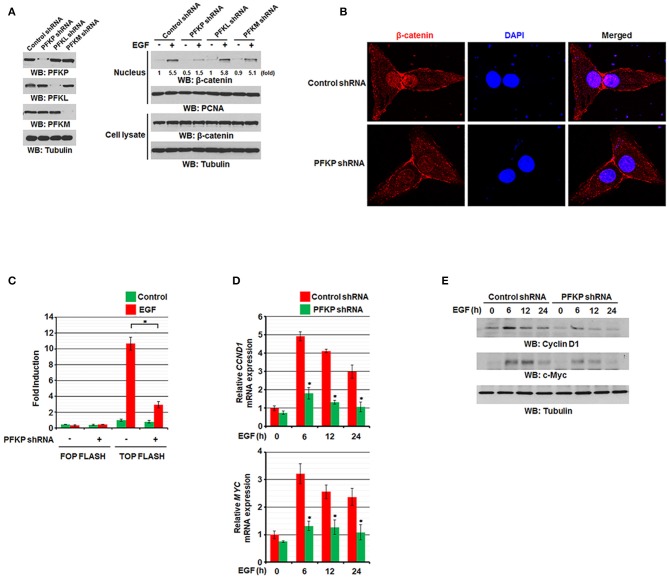
Figure 1.
PFKP expression is required for EGFR activation-induced nuclear translocation and transactivation of β-catenin. (A) Serum-starved U87/EGFR cells with the indicated shRNAs (left panel) were treated with or without EGF (100 ng/ml) for 9 h. The cells were harvested for the isolation of nuclear fractions (right panel). Immunoblotting analyses were performed with the indicated antibodies. (B) U87/EGFRvIII cells were stably expressed with control shRNA or PFKP shRNA. Immunofluorescent staining was performed with an anti-β-catenin antibody. (C) U87/EGFR cells with or without PFKP depletion were transfected with TOP-FLASH or FOP-FLASH, which was followed by EGF treatment for 6 h. Luciferase activity was measured. The relative levels of luciferase activity were normalized to the levels of untreated cells and to the levels of luciferase activity in the Renilla control plasmid. Data represent the means ± SD of three independent experiments. *P < 0.001, based on the Student's t-test. (D,E) Serum-starved U87/EGFR cells with or without depleted PFKP were treated with or without EGF for the indicated periods of time. The mRNA expression levels (D) and the protein expression levels (E) of CCND1 and MYC in U87/EGFR cells were determined by real-time PCR and immunoblotting analyses with the indicated primers and antibodies, respectively. Data represent the means ± SD of three independent experiments. *P < 0.001, based on the Student's t-test.