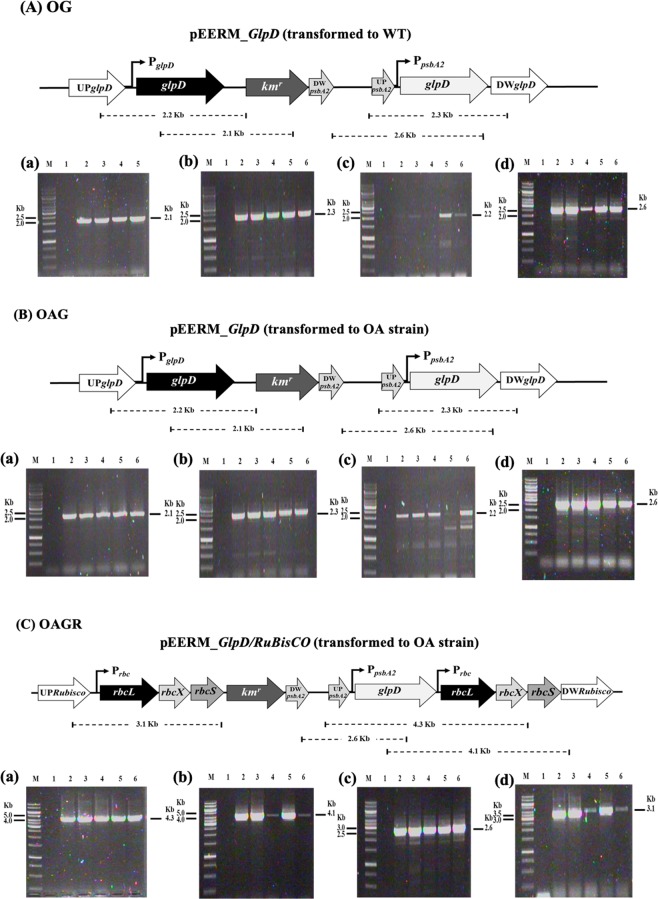
Figure 2.
Genomic maps of engineered Synechocystis PCC 6803 strains, including the overexpression strains OG (A), OAG (B), and OAGR (C). The specific primers (Supplementary information, Table S1) are used for confirming the integration of each gene into Synechocystis genome. The OA strain3 was singly recombined with the aas gene. The OG and OAG strains were constructed by overexpressing the native glpd gene in WT and OA cells, respectively. OAGR was generated by overexpressing glpd and a RuBisCo cassette in the OA strain. Confirmation of integration was performed using PCR with genomic DNA from WT and engineered strains as the template. Lane M: GeneRuler DNA ladder (FERMENTAS). For (A) OG strain; Lane 1: negative control using WT as template (a–d), (a) Lanes 2–5: clone numbers 1 to 4 using Glpd_SF and Km_SR primers, (b) Lanes 2–6: clone numbers 1 to 5 using USpsbA2 and DSglpD primers, (c) Lanes 2–6: clone numbers 1 to 5 using USglpD and bb_cSR primers, and (d) Lanes 2–6: clone numbers 1 to 5 using bb_f1 and Glpd_SR primers. For (B) OAG strain; Lane 1: negative control using WT as template (a–d), (a) Lanes 2–6: clone numbers 1 to 5 using Glpd_SF and Km_SR primers, (b) Lanes 2–6: clone numbers 1 to 5 using USpsbA2 and DSglpD primers, (c) Lanes 2–6: clone numbers 1 to 5 using USglpD and bb_cSR primers, and (d) Lanes 2–6: clone numbers 1 to 5 using bb_f1 and Glpd_SR primers. For (C) OAGR strain; Lane 1: negative control using WT as template (a–d), (a) Lanes 2–6: Lanes 2–6: clone numbers 1 to 5 using USpsbA2 and RBC_SR2 primers, (b) Lanes 2–6: clone numbers 1 to 5 using GlpD_SF and DSrubisco primers, (c) Lanes 2–6: clone numbers 1 to 5 using bb_f1 and Glpd_SR primers, and (d) Lanes 2–6: clone numbers 1 to 5 using USrubisco and bb_cSR primers.