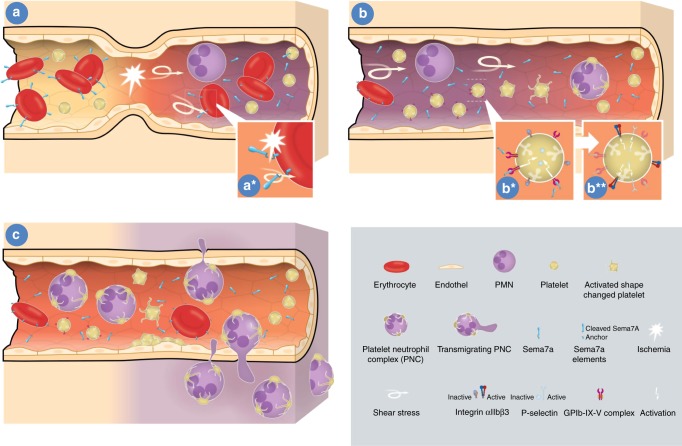
Fig. 7. Schematic drawing of the role of Sema7a during myocardial IR.
a During myocardial ischemia shear stress and hypoxia result in cleavage of Sema7a from the surface of erythrocytes as the main source of Sema7a within the vascular bed. b The released Sema7a then engages the Glycoprotein Ib receptor and activates platelets which then exposes the integrin receptors resulting in platelet–neutrophil complex formation (PNCs). c Activated platelets and PNCs migrate from the vasculature to the ischemic tissue which results in tissue injury and destruction.