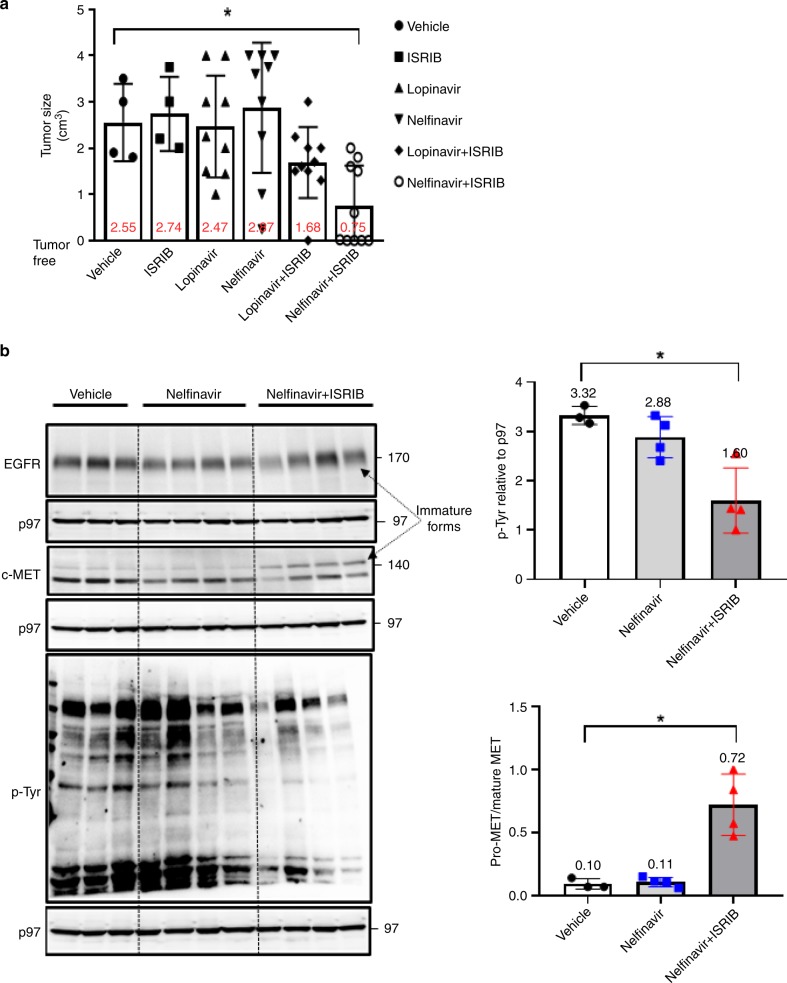
Fig. 6. Nelfinavir in combination with ISRIB significantly diminishes tumor size without causing a noticeable hepatotoxicity.
a NOD-SCID mice were subcutaneously injected with HepG2 cells (two million cells/mouse). Three days following the xenografts injection, mice were treated daily either with vehicle, ISRIB (2.5 mg/kg), lopinavir (17 mg/kg), nelfinavir (50 mg/kg), lopinavir + ISRIB, or nelfinavir + ISRIB for 14 days. Tumors dimensions were measured with a caliper. Data are shown in whisker-diagram as a tumor size (cm3) for each treatment (four mice were used for vehicle and ISRIB groups and nine animals for the other groups). Averages are indicated. Error bars represent SD. p < 0.05 was obtained only for nelfinavir/ISRIB treatment by one-way ANOVA test. b NOD-SCID mice bearing 10 days old subcutaneous HepG2-derived xenografts were intraperitoneally injected with vehicle, nelfinavir, or nelfinavir/ISRIB twice a day for three consecutive days. Tumor were excised and immunoblotting to EGFR, c-MET, p-Tyr, and p97 was performed (left). Shown is the quantified total p-Tyr levels relative to p97 as loading control for each mouse and the pro-MET to mature MET ratio, indicative for sERr efficiency. N = 3 for vehicle and N = 4 for nelfinavir or nelfinavir/ISRIB groups. Average values are indicated. Bars represent SD. Error bars represent SD. *p < 0.05 by Kruskal–Wallis one-way analysis of variance.