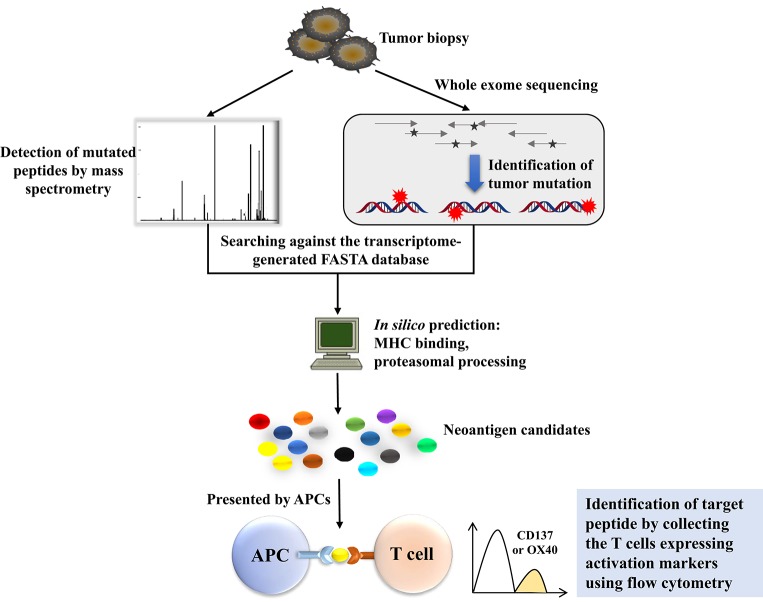
Figure 2.
The workflow of neoantigen screening using whole-exome sequencing (WES) combined with mass spectrometry (MS). WES is conducted to identify the tumor-specific mutations, together with mass spectrometry-based mutated peptide detection, to compare the mutated proteins with those in the transcriptome-generated FASTA database. Mutated proteins will be predicted in silico to narrow down the target mutations. Predicted peptides can be expressed by a patient's APCs, where they are processed and presented in the context of a patient's MHC. The coculture of the patient's autologous T cells with these APCs can be used to identify the mutations processed and presented by APCs. The identification of individual mutations for tumor recognition is applicable because T cells express activation markers such as OX40 or CD137 when they recognize the cognate target antigen.