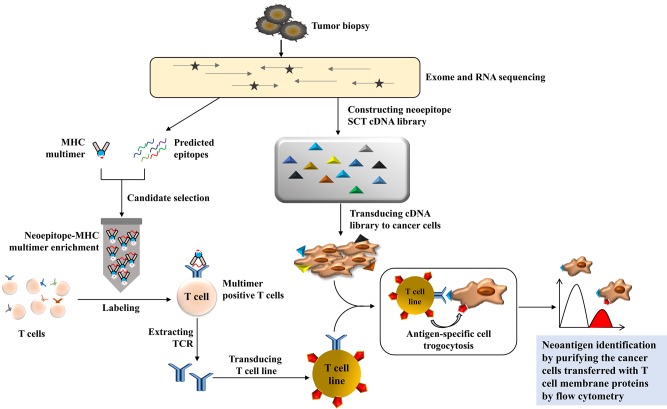
Figure 4.
The illustration of neoantigen screening via trogocytosis. The private mutations are identified by exome and RNA sequencing from tumor samples, and the neoepitope ligand can be predicted and presented by an MHC multimer panel to be applied to the patient's autologous T cells. The gene of neoepitope-reactive TCR can be verified and transduced into a T cell line as an effector cell line. Meanwhile, the neoepitope single-chain trimer (SCT) cDNA library can be generated and transduced into K562 or other cancer cell lines to construct the target cell library. The coculture of effector cells with the target cell library will be used to identify the neoepitope because the membrane protein from the T cell line will transfer to the specific target cell whenever the neoantigen matches the T cell with a specific TCR. After two rounds of flow cytometry-based cell sorting, the neoantigen for tumor recognition can be isolated based on the specific membrane protein transferred to neoepitope-transduced target cells.