Figure 2.
5430416N02Rik RNA Is Required for the Chromatin Interactions at Its Promoter
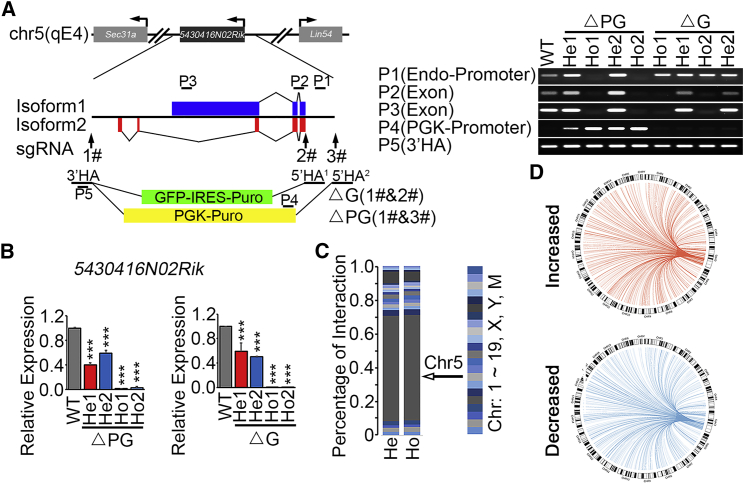
(A) Schematic illustration of knockout strategy at the 5430416N02Rik locus. Two isoforms of 5430416N02Rik are shown with blue and red boxes, respectively. The gene body and the promoter (~2 kb upstream of TSS) of 5430416N02Rik are replaced by a PGK-puro cassette, resulting in homozygous (Ho) or heterozygous (He) ΔPG ESCs. In ΔG cells, only the gene body is replaced by a GFP-IRES-Puro cassette. He1&2 and Ho1&2 are two independent heterozygous and homozygous clones, respectively. Vertical arrows mark targeting sites of three sgRNAs. Homology arms (3′ HA, and 5′ HA1 and 5′ HA2) are shown in bold. Short black lines, P1 to P5, marks PCR amplicon for genotyping. The bottom panel shows the genotyping results.
(B) 5430416N02Rik expression levels in heterozygous and homozygous ΔPG and ΔG ESCs, as well as WT ESCs, detected by qRT-PCR. Three biological replicates per sample were assayed. Data are shown as the mean ± SEM (n = 3). ∗∗∗p < 0.001, t test.
(C) Numbers of interacting sites with the 5430416N02Rik promoter in individual chromosomes identified by Capture-C-seq are shown in 100% stacked column.
(D) Circos plots of differential 5430416N02Rik-interacting sites in homozygous ΔG ESCs, compared with heterozygous ΔG ESCs, identified by Capture-C-seq. Two biological replicates were performed for each Capture-C experiment.