Fig. 2. Gαs-coupled DRD1 is selectively expressed in pulmonary fibroblasts.
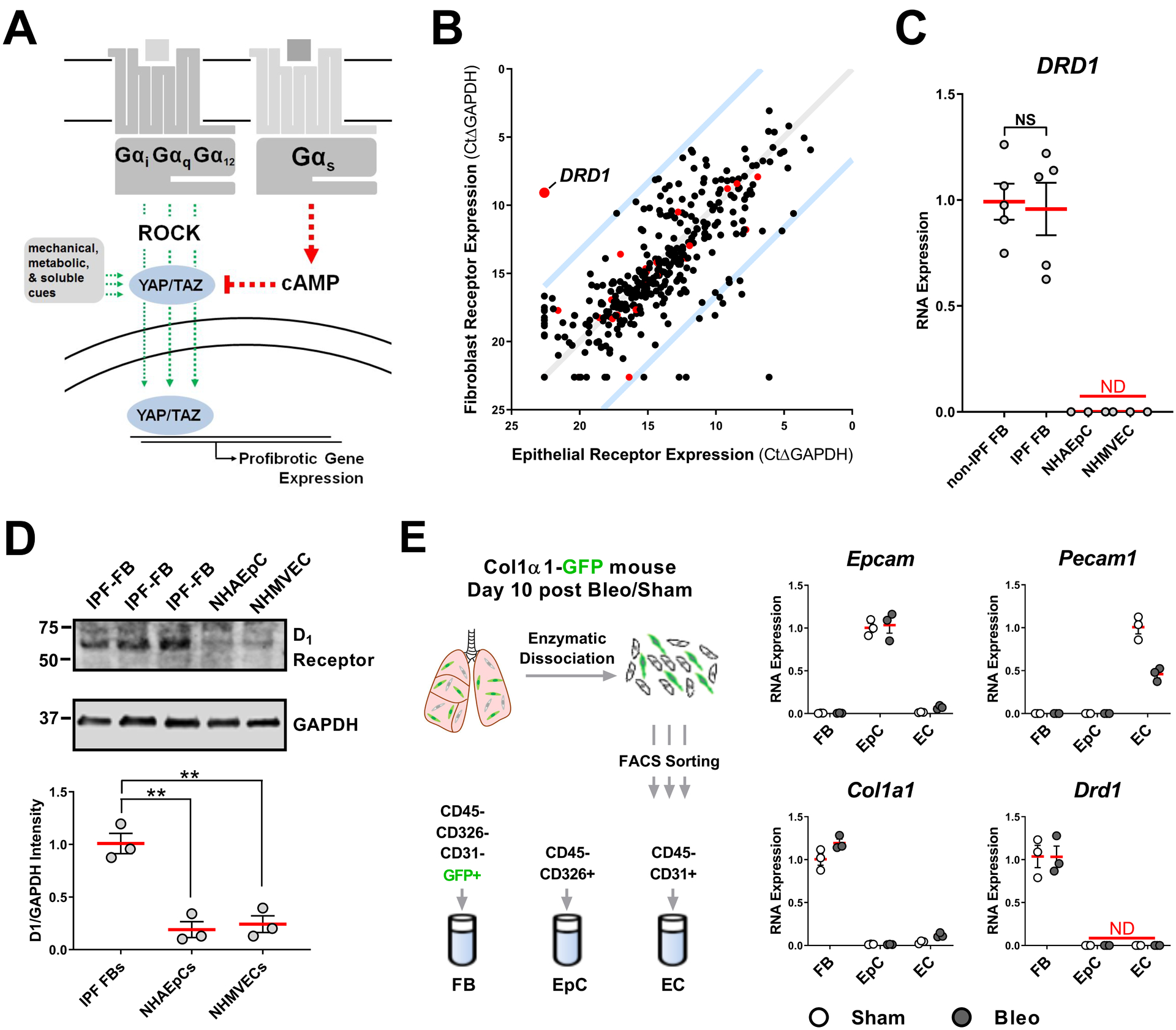
A. Receptors that couple to Gαs elevate cAMP and induce phosphorylation of YAP/TAZ, blocking nuclear localization. Receptors that couple to Galphαi/q/12 promote nuclear localization and activity of YAP/TAZ, as do other mechanical, metabolic and soluble cues, through Rho-kinase (ROCK) and other pathways. B. GPCR expression profile of primary cultured human alveolar epithelial cells and normal human pulmonary fibroblasts. Red points indicate GPCRs that selectively couple to Gαs. Blue lines indicate 100-fold preferential expression. C. DRD1 expression in cultured non-IPF associated fibroblasts (N=5 biologically independent samples), IPF patient-derived fibroblasts (N=5 biologically independent samples), normal human alveolar epithelial cells (NHAEpC)(N=3 biologically independent samples), and normal human microvascular endothelial cells (NHMVEC) (N= 3 biologically independent samples), all passage 6 or less. D. Western blot protein expression of the D1 dopamine receptor from IPF patient derived fibroblasts, normal human alveolar epithelial cells (NHAEpC), and normal human microvascular endothelial cells (N=3 biologically independent samples). E. Expression of Drd1 in freshly isolated mouse lung fibroblasts (FB), epithelial (EpC), and endothelial cells (EC). Lung from sham or Day 10 post bleomycin treated Col1a1-GFP expressing mouse was enzymatically digested then sorted for markers of epithelial cells (validated by Epcam expression), endothelial cells (validated by Pecam1 expression), and fibroblasts (validated by Col1a1 expression) followed by RNA isolation and qPCR for Drd1. N=3 mice/group (comparisons made using ANOVA, ** p < 0.01 vs. indicated group).
