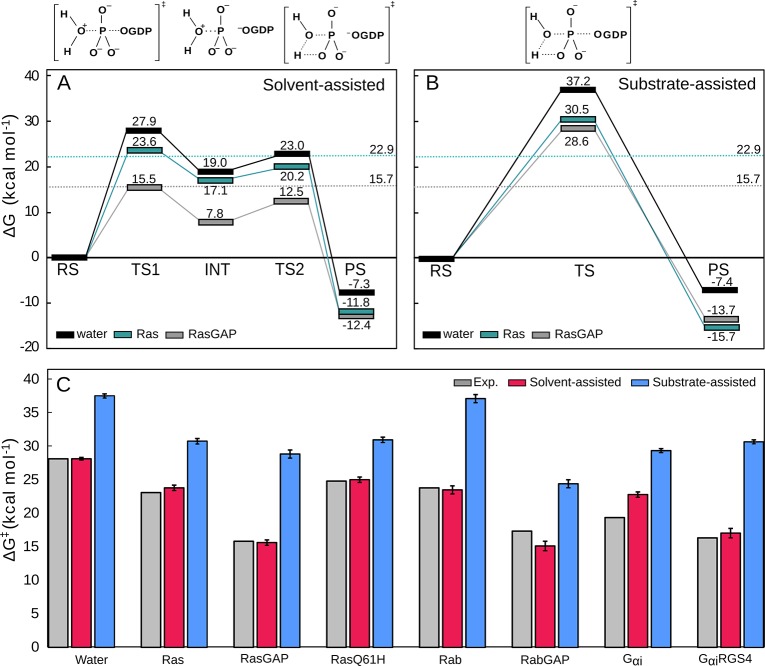
Figure 3.
Calculated free energy profiles for the (A) solvent- and (B) substrate-assisted hydrolysis of GTP in aqueous solution, and as catalyzed by Ras and the RasGAP complex. (C) Activation free energies for each of the two mechanisms, as catalyzed by a range of GTPases (Ras, Rab and Gαι, both with and without their corresponding regulatory proteins, as well as the Ras Q61H mutant). Note that as shown in panel A, the initial phosphoryl transfer reaction in the solvent-assisted hydrolysis of GTP leads to a short-lived intermediate (INT), which will then tautomerize to yield the final product, which is chemically identical to the final product state for the substrate-assisted pathway. A similar pathway was observed in quantum chemical calculations of phosphate esters in aqueous solution.8−10 For further details, see ref (7). Reprinted with permission from ref (7) (direct link: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacs.9b03193). Copyright 2019 American Chemical Society.