Fig. 1.
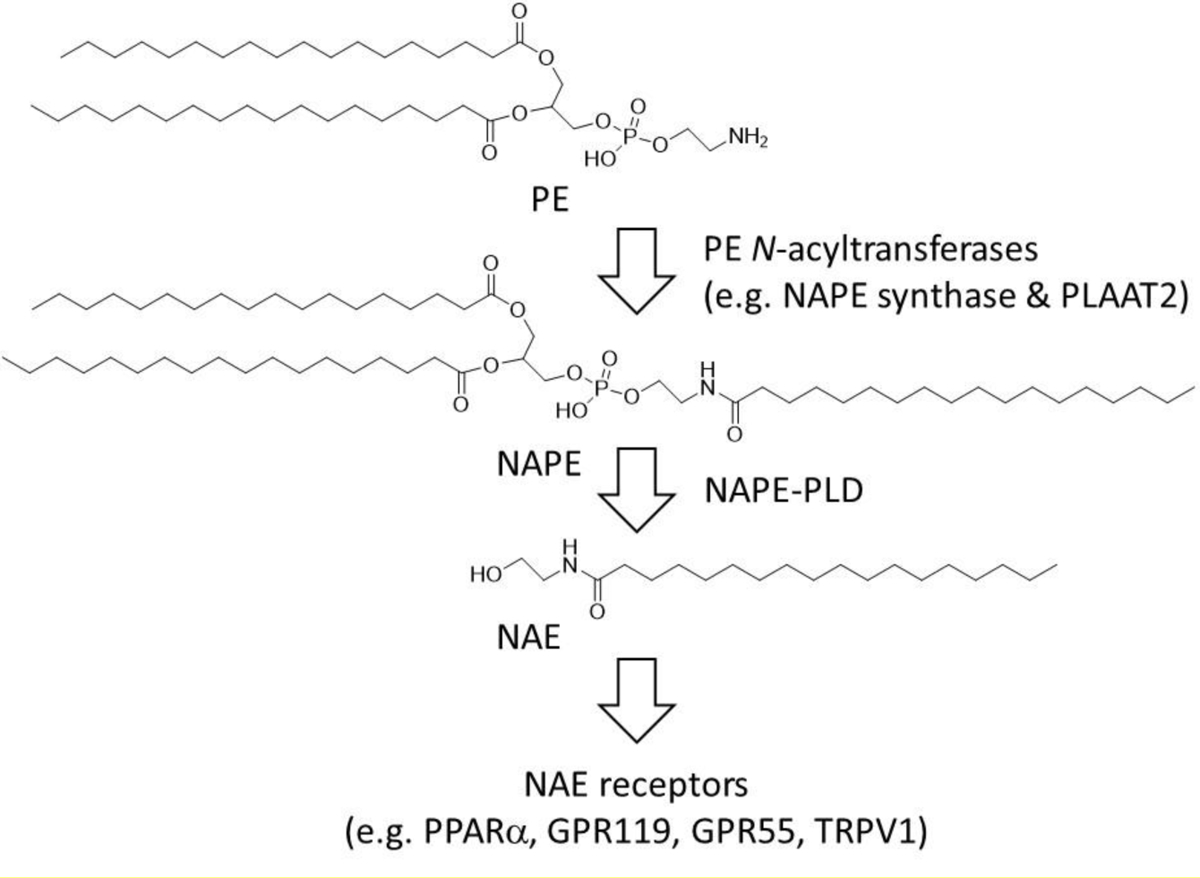
Biosynthetic and signaling pathways for N-acyl-ethanolamides (NAEs). Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) N-acyltransferase enzymes transfer an acyl chain from a donor phospholipid to PE to form N-acyl-phosphatidylethanolamines (NAPE) which are then converted by NAPE hydrolyzing phospholipase D (NAPE-PLD) to NAEs, which in mammals act on receptors including PPARα, GPR119, GPR55, and TRPV1.
