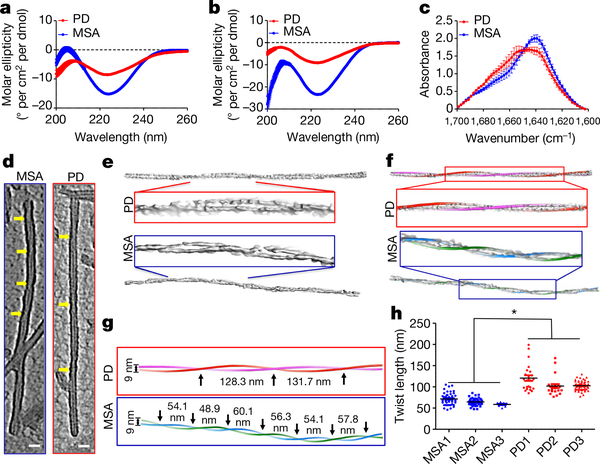
Fig. 3 |. Structural differences between α-syn aggregates derived from patients with PD or patients with MSA.
a, Circular dichroism spectra of α-syn aggregates from the CSF of patients with PD (red) or patients with MSA (blue), amplified by two rounds of α-syn-PMCA. Spectra were recorded from 35 μM suspensions of α-syn aggregates, as described in Methods. Measurements were taken for all of the PD (n = 43) and MSA (n = 43) samples analysed and data (molar ellipticity) are mean ± s.e.m. b, A similar experiment was performed for α-syn aggregates that were amplified from the brain of patients with PD (n = 3) or patients with MSA (n = 3). c, FTIR spectra of α-syn aggregates that were obtained after two rounds of seeding and amplification of samples of CSF from patients with PD (n = 10) or patients with MSA (n = 10). The solution of aggregated proteins (5 μl; 5 mg ml−1) was analysed with an FTIR-4100 spectrometer (JASCO). d, Cryo-ET was performed to evaluate structural differences between fibrils from patients with PD and fibrils from patients with MSA. Central slices of representative subtomograms of PD-associated fibrils and MSA-associated fibrils are shown. The negative-stained fibrils were imaged with a 300-kV electron microscope (Methods). Yellow arrows indicate twists in the filaments. Scale bar, 20 nm. e, Three-dimensional density maps segmented from the original tomograms. Boxed densities are magnified views. f, Three-dimensional helical models were built that overlapped with the corresponding densities of PD- and MSA-associated fibrils, including a magnification of the central region. g, Helical models showing the periodicity of twisting of PD- or MSA-associated fibrils. Black arrows indicate the twist in the 3D model of the filament. h, Quantification of the periodic spacing (in nm) in many different fibrils derived from samples from patients with PD (n = 3) or patients with MSA (n = 3) samples. Each dot corresponds to a different fibril and data are mean ± s.e.m. *P < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test.