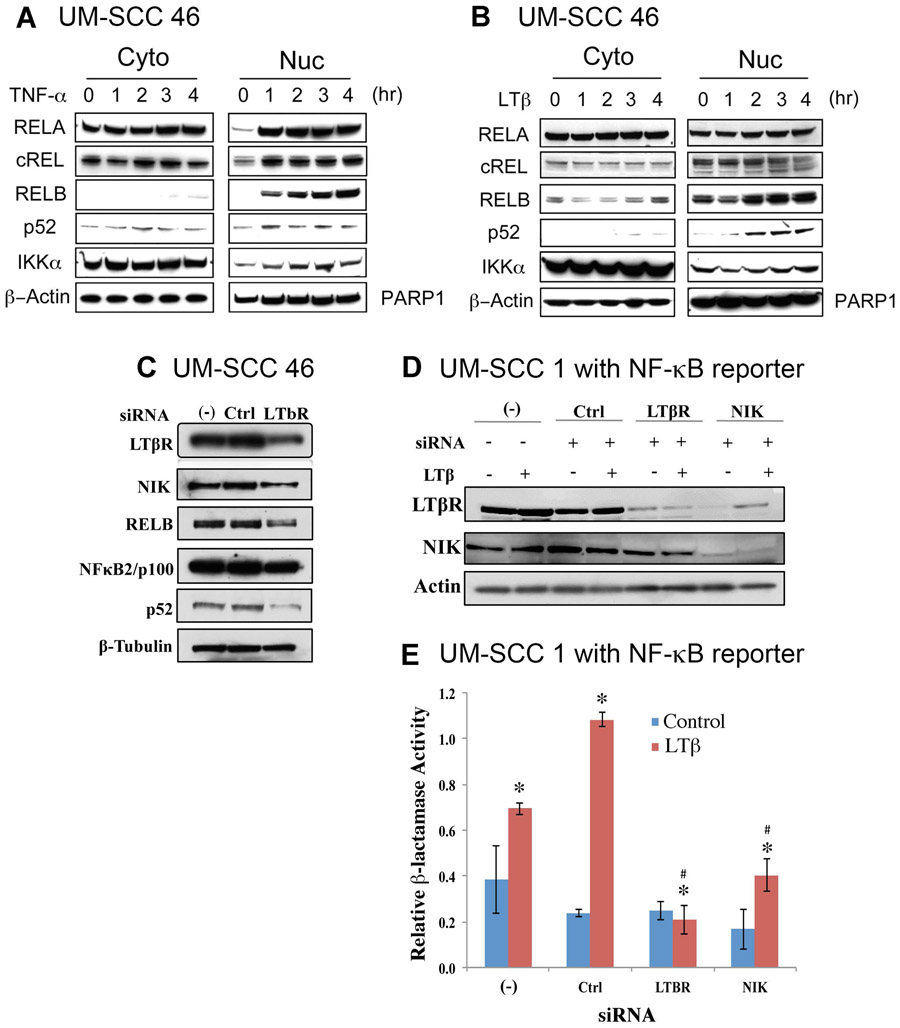
Figure 2. TNF-α and LTB stimulated and LTβR and NIK knocking down inhibited NF-κB proteins and function activity in HNSCC cell line.
The HNSCC cell line UM-SCC 46 was treated with TNFα (25ng/ml, A) or LTβ (100ng/ml, B), and the protein levels of NF-κB subunits were measured at different time points via Western blot. β-actin was used as a loading control for the cytoplasmic fraction, and PARP1 for the nuclear fraction. (C) Knockdown of LTβR modulated its target kinase NIK, RELB, NF-κB2/p100/p52 protein expression in UM-SCC-46 cells. Cells were transfected with LTβR siRNA, whole cell lysates were harvested 96h after transfection, and measured for LTβR, NIK, RELB and NF-κB2/p100/p52 by Western blot. β-tubulin was used as loading control. (D) Protein expression of LTβR and NIK after knockdown of LTBR and NIK by siRNAs in stable NF-κB Blazer Reporter UM-SCC-1 stable cell line. Whole cell lysates were harvested by sonication of samples from each well of the β-Lactamase assay plate. Western blot was performed and β-Actin was used as loading control. (E) Knockdown of LTBR and NIK by siRNAs affected NF-κB reporter function in NF-κB Blazer Reporter UM-SCC-1 stable cell line. Relative β-Lactamase units were measured after stimulation with LTβ (100ng/ml) for 24h before harvesting the cells at 96h. * indicates statistical significance induced by LTB treatment, and # indicates statistical significance after siRNA knockdown (p-value<0.05 by t-test). Data were calculated from triplicates of a representative experiment.