Figure 2.
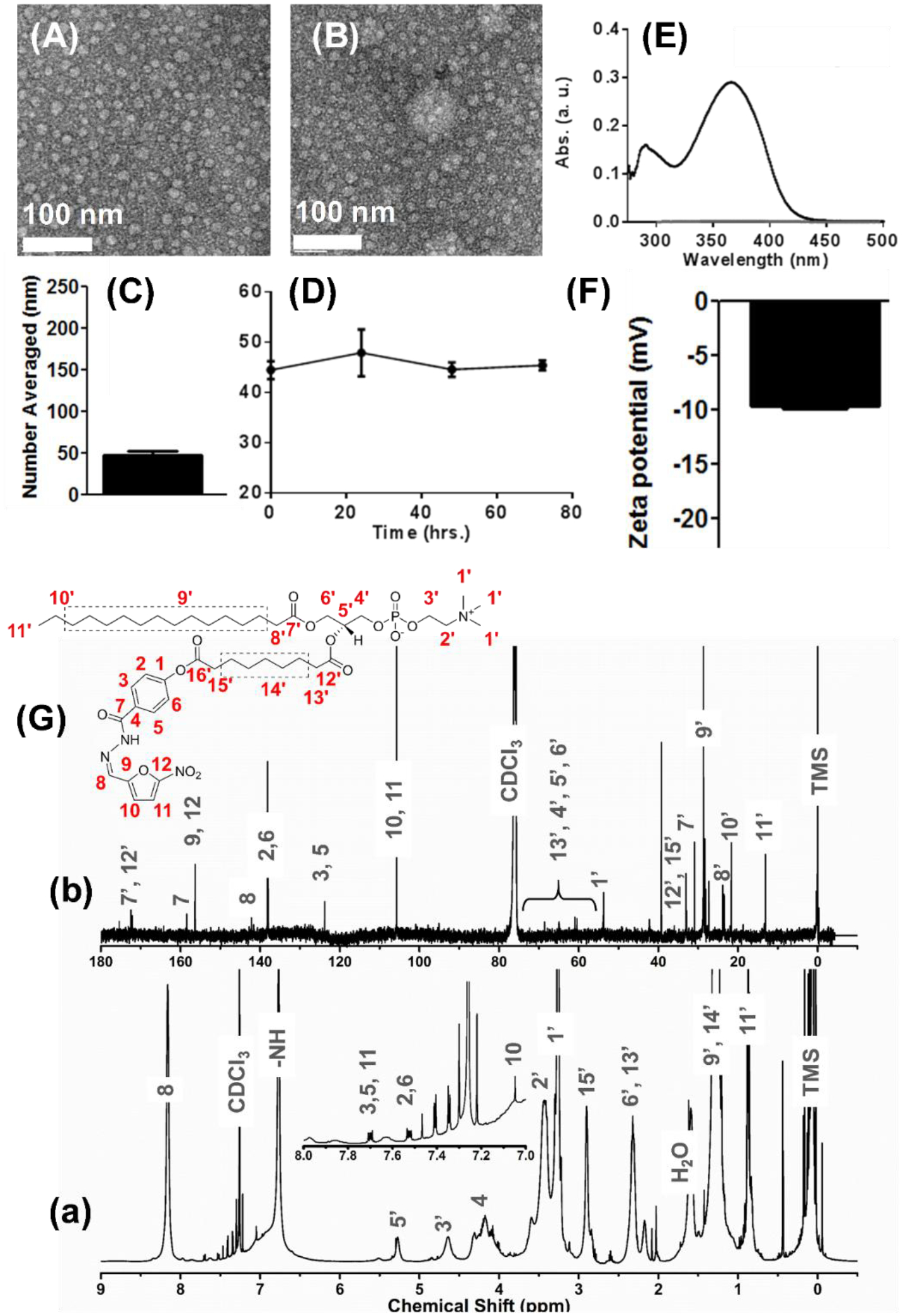
Physicochemical characterization of different chemistries and formulations of Nifuroxazide. (A-B) Anhydrous morphology of Pro-nifuroxazide nanoparticles (NPs) obtained using transmission electron microscopy in negative staining mode (TEM, uranyl acetate) from different section of electron grids. (C) Hydrodynamic diameter of Pro-nifuroxazide NP and (D) stability of the self-assembled Pro-nifuroxazide nanoparticle (pH 7.4). (E) UV-vis spectrum of free nifuroxazide molecules in water revealing characteristic absorbance of the drug molecule. (F) Zeta potential; (G) nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra of the Pro-nifuroxazide (a) 1H and (b) 13C traces (CDCl3).
