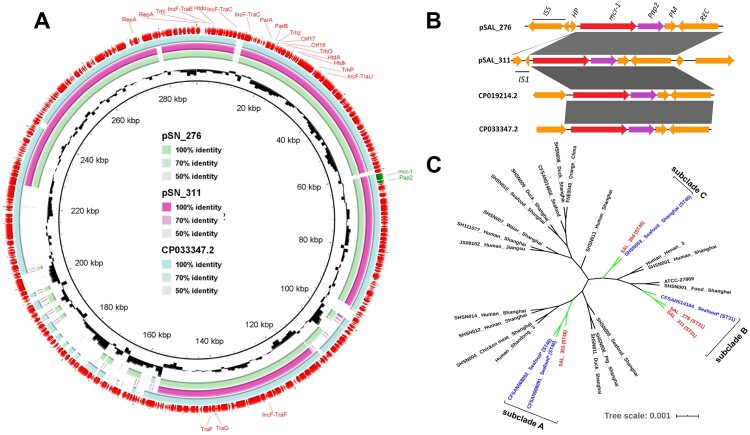
Figure 1.
Comparative sequence analysis of the mcr-carrying plasmids and phylogenomic features for all Chinese Salmonella Newport genomes available in the NCBI database in addition to four new colistin-resistant strains in this study. (a) Sequence comparison of two reconstructed mcr-1-positive plasmids from whole-genome sequence. The out layer circle refer to the CP01924.2 plasmid. (b) Genetic backbone flanking with mcr-1 sequence of SAL_276 and SAL_311 (CP019214.2 in E. coli isolated from sewage in China and CP033347.2 in S. Typhimurium isolated from pork in China). IS, insertion sequence; HP, hypothetical protein; PM, putative membrane; REC, recombinase. (c) Phylogenomic analysis of all available S. Newport Chinese isolates in this study, including 24 additional Chinese S. Newport isolates from different hosts retrieved from the NCBI database. The four isolates examined in this study in addition to their closely related seafood-origin isolates were clustered together in the three subclades (A, B and C). Tree scale represents the genetic distance between the isolates used to construct the tree. *These isolates were collected by US FDA, mentioning China as their place of origin.