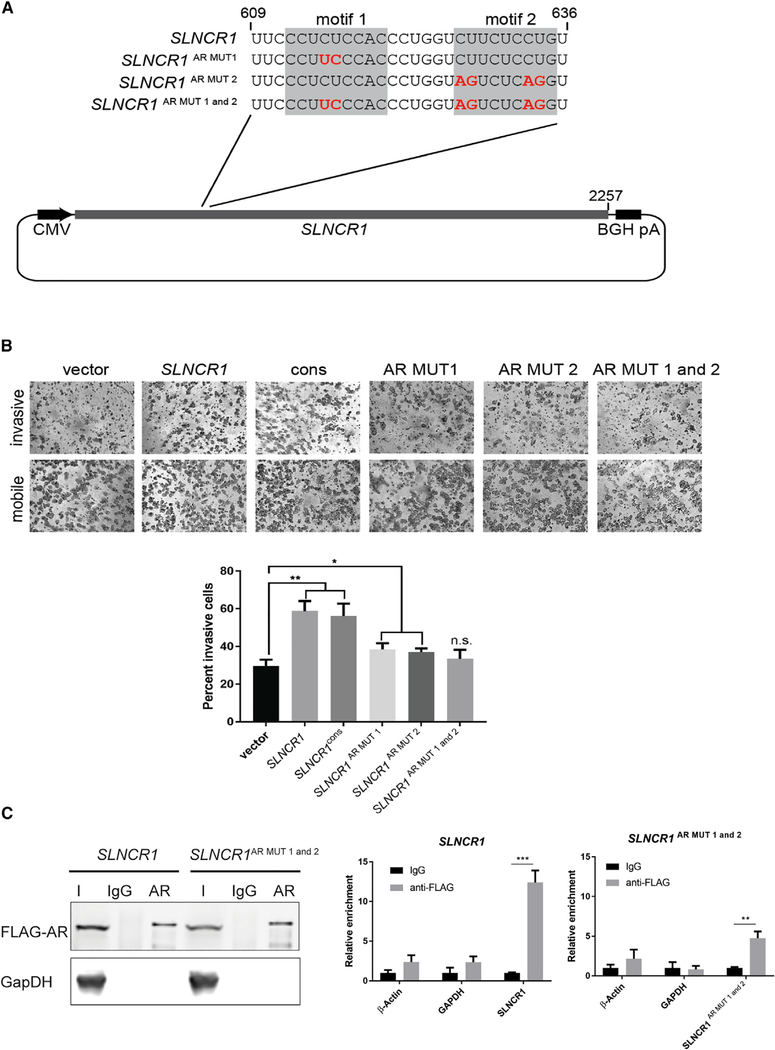
Figure 6. Mutation of the AR-Binding Motif Blocks SLNCR1-Mediated Invasion.
(A) Schematic of the SLNCR1 sequences expressed in (B), zoomed in on the region containing site-directed mutations within the AR-binding motif.
(B) Matrigel invasion assays of A375 cells transfected with either an empty vector or a vector expressing the indicated SLNCR1 sequence. SLNCR1cons corresponds to SLNCR1 nucleotides 372–672. Invasion is calculated as the percent of invading cells compared to mobile cells as counted in eight fields of view. Top panels show representative images of the indicated invading and mobile cells. Quantification from three independent replicates, represented as mean ± SD, is shown at the bottom.
(C) RNA IP assaysfrom HEK293T cellstransfected with FLAG-tagged ARand the indicated SLNCR1-expressing plasmids using either α-FLAG orIgG nonspecific control. Left panel: western blot analysisofinput (I), IgG-bound (IgG), or α-FLAG bound (AR) proteins. Right panel: relative enrichment represented as mean ± SD of the indicated transcripts from FLAG-AR IPs compared to the nonspecific IgG control. Significance was calculated using the Student’s t test: *p < 0.05; **p < 0.005; ns, not significant.
See also Figure S7.