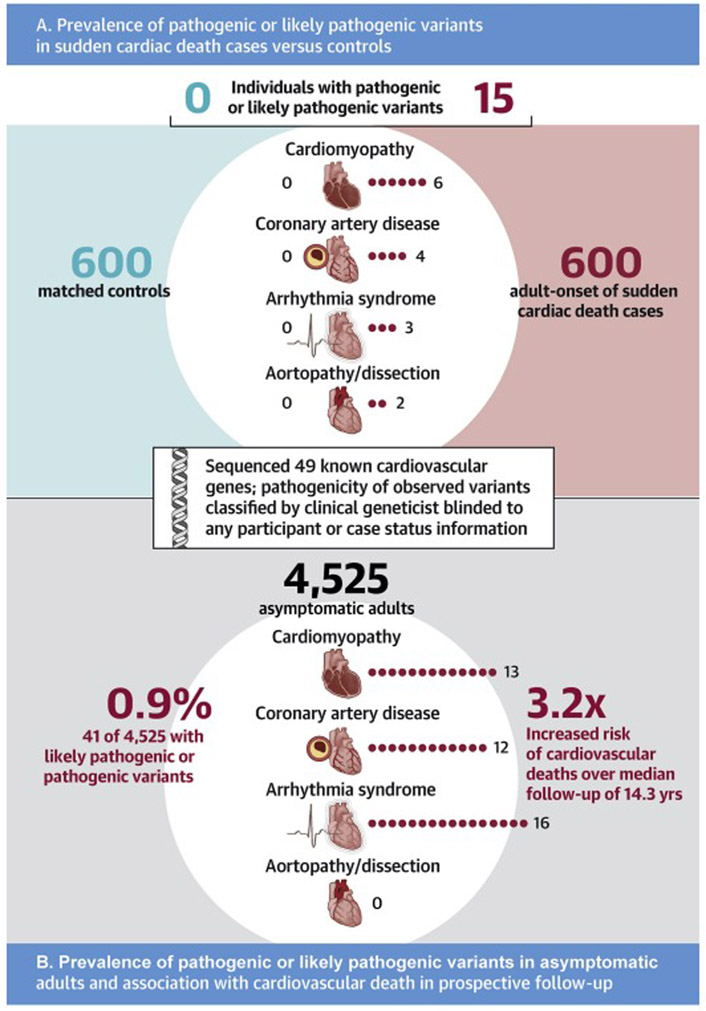
Central Illustration. Gene sequencing to identify pathogenic variants in sudden cardiac death cases versus controls, and in asymptomatic adults.
A. In an adult-onset sudden cardiac death case-control cohort, whole exome sequencing identified pathogenic or likely pathogenic variants in 15 (2.5%) of cases versus 0 (0%) of controls (p<0.0001). The number of carriers of a pathogenic or likely pathogenic variant observed in each of four important conditions underlying sudden cardiac death is displayed according to case versus control status. Test of statistical significance was performed for the combined variant counts using a Fisher’s exact test. B. Among 4,525 asymptomatic adult participants of the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis free of known cardiovascular disease, whole genome sequencing identified 41 (0.9%) with a pathogenic or likely pathogenic variant – the number of carriers of a pathogenic or likely pathogenic variant observed in each of four important conditions underlying sudden cardiac death is displayed. Over a median follow-up of 14.3 years, these 41 carriers had a 3.24-fold (p=0.02) increased risk of incident cardiovascular death, as assessed in a Cox proportional hazards model adjusted for age, sex, and race.