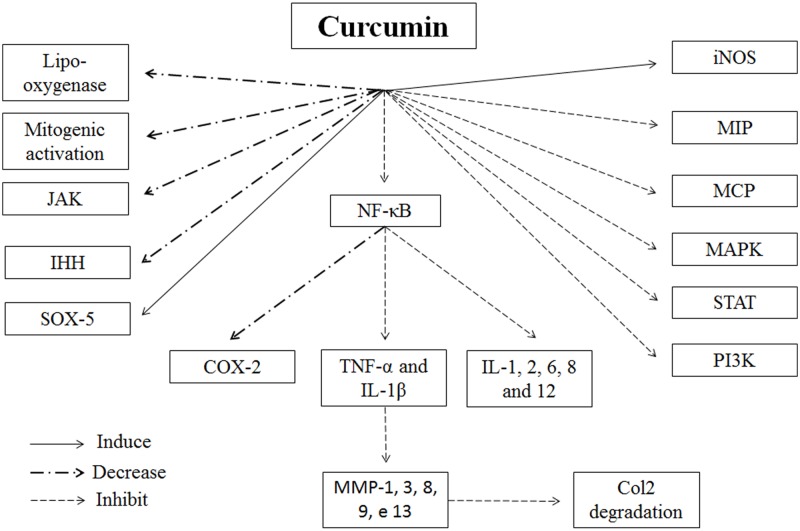
Fig 1. Diagrammatic representation of the curcumin role on inflammation and Col2 degradation.
The curcumin decreases lipo-oxygenase, mitogenic activation, JAK (Janus Kinase), IHH (Indian hedghog) and also COX-2 (cyclo-oxygenase-2) via NF-ΚB inhibition. The curcumin induces SOX-5 and iNOS (induced nitric oxide synthase). The curcumin inhibit MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase), MCP (monocyte chemoattractant protein), STAT (signal transduction and activation transcription), PI3K (phosphoinositide 3-kinase), MIP (Migration inhibitory protein). The expression of IL-1, 2, 6, 8 and 12 (interleukin), TNF-α (Tumour Necrosis Factor alpha) and IL-1β are inhibited via NF-ΚB (nuclear factor kappa B) inhibition. The MMP-1, 3, 8, 9 and 13 (matrix metalloproteinases) are mainly inhibited via TNF-α and IL-1β inhibition which leads to an inhibition in Col2 degradation.