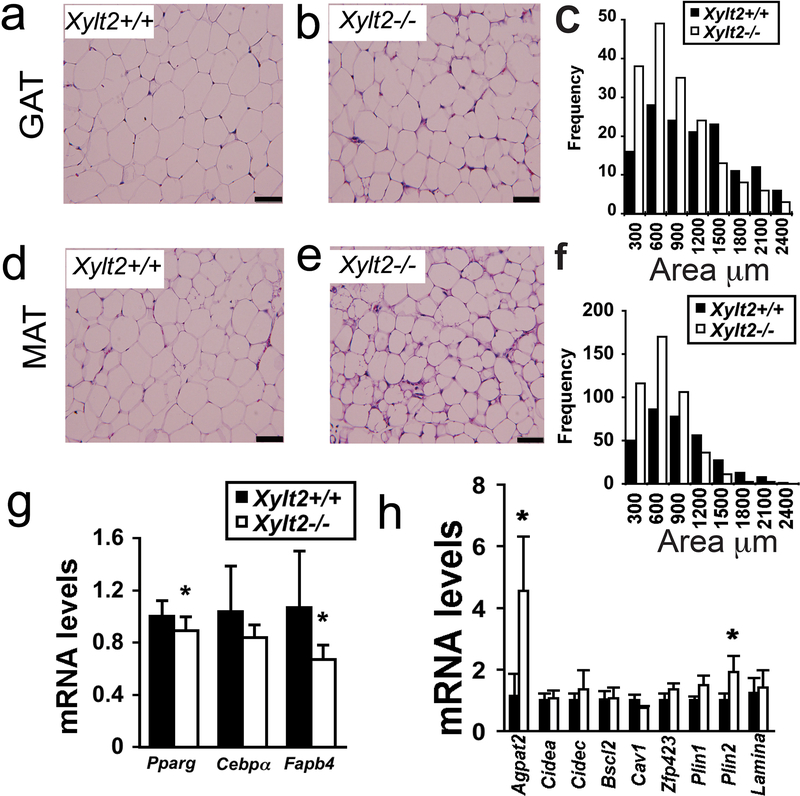
Figure 2.
Adipocyte morphology, gene expression, and GAG content with XylT2 deficiency in 2–3 month male mice. Adipocyte morphology was assessed by hematoxylin and eosin staining of GAT. (a) Xylt2+/+ and (b) Xylt2−/− mice followed by (c) adipocyte size distribution measurements, n=4 of each genotype. (d)(e)(f) Similar analyses in MAT, n=4 of each genotype, scale bars = 100μm. (g) GAT expression of adipogenic differentiation factors peroxisomal proliferation activator receptor-γ (Pparg), CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-α (Cebpa), and fatty acid binding protein four (Fabp4) in GAT (n=4 of each genotype). (h) GAT expression analyses of known lipodystrophic genes in Xylt2+/+ and Xylt2−/− mice. * p<0.05.