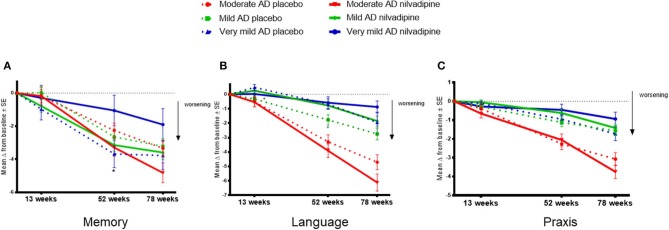
Figure 4.
Nilvadipine treatment effects on cognitive traits. Very mild AD subjects show less decline on the memory trait, whereas mild AD subjects show less decline on the language trait, after nilvadipine treatment compared to placebo. Mean ± SE (n = 82 for moderate AD on nilvadipine, n = 94 for moderate AD on placebo, n = 118 for mild AD on nilvadipine, n = 113 for mild AD on placebo, n = 36 for very mild AD on nilvadipine, n = 44 for very mild AD on placebo) for the change in memory, language and praxis traits of grouped ADAS-cog 12 sub-scales. (A) There was a significant effect for the interaction between treatment, time and baseline AD severity on the memory trait. post-hoc stratifications by time show that very mild AD subjects treated with nilvadipine had significantly less decline on the memory trait compared to their controls. (B) There was also a significant interaction between treatment, time and baseline AD severity for the language trait. post-hoc stratifications by time show that mild AD subjects treated with nilvadipine had less decline on the language trait compared to the placebo-treated mild AD subjects. (C) There was no effect seen for the praxis trait. *p < 0.05.