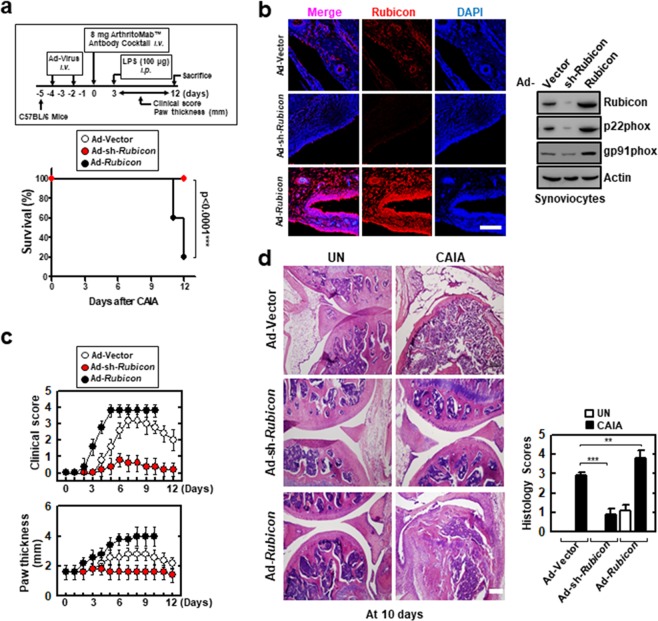
Figure 2.
Alteration of Rubicon gene expression affects CAIA mice mortality. (a) Schematic of the collagen antibody-induced arthritis (CAIA) model (upper). At 48 hr post-injection with Ad-GFP, Ad-shRubicon, or Ad-Rubicon (1 × 1013 pfu/kg), twice intravenously via the tail vein, CAIA mice model was established. The survival of CAIA mice was monitored for 12 days and mortality was measured for n = 10 mice per group (lower). Statistical differences, as compared to the Ad-GFP-injected mice, are indicated (log-rank test). (b) Immune-stained with αRubicon or DAPI for Rubicon gene expression (left). IB with αRubicon, αp22phox, or αActin (right). Scale bars: 100 μm. (c) Clinical arthritis score and swelling of paws. Data shown are the means ± SD of three experiments. (d) Representative H&E staining of the ankle joints of each group determined at 9 days of CAIA (left). Scale bars: 200 μm. Histopathology scores (right) from ten mice per group. Statistical significance was determined by two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s posttest; ***P < 0.001 compared with Ad-Vector (a). Data shown are the means ± SD of three independent experiments (c). UN, untreated.