Figure 1.
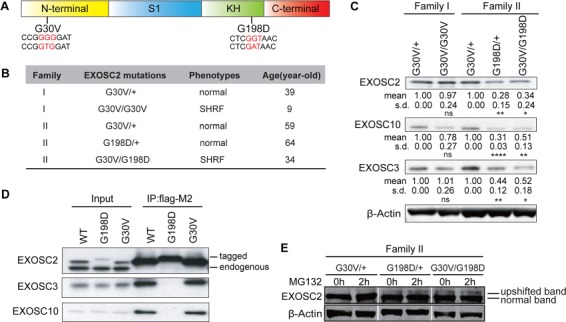
EXOSC2 mutations differentially affect protein stability and protein interactions. (A) EXOSC2 protein schematic domains and mutations. S1, KH domains are RNA-binding domains. G30V mutation (GGG to GTG) and G198D mutation (GGT to GAT) are labeled in red. (B) Family, genotype, phenotype and diagnosed age information of EXOSC2-mutated individuals. (C) Western blot of EXOSC2, EXOSC3 and EXOSC10 protein levels in B-lymphoblast cells from two EXOSC2 mutated families. Quantification of protein levels is provided under each blot. *, ** and **** indicate P < 0.05, P < 0.01 and P < 0.0001, respectively, in Student’s t test (n = 4). n.s, non-significant; s.d, standard deviation. (D) Co-immunoprecipitation between EXOSC2-FLAG and EXOSC3/EXOSC10 in HEK293T cells. (E) Western blot of EXOSC2 level from MG132-treated family II B-lymphoblasts. Note that although a much fainter upper band is visible in the G30V/+ samples, it is likely that this is some non-specific signal recognized by the EXOSC2 antibody rather than some unknown posttranslational modification of EXOSC2 that causes the upshift, since the tagged EXOSC2s do not produce such additional band (D).
