Figure 4.
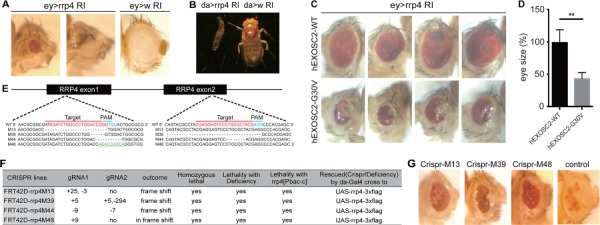
Phenotypic characterization of rrp4 loss-of-function fly mutants. (A) Microphotographs of fly eyes in which the fly rrp4 gene was knocked down by ey-Gal4>UAS-rrp4 RNAi (ey>rrp4 RI); ey-Gal4>UAS-white RNAi (ey>w RI) was used as a control. (B) Whole body images of animals with ubiquitous knockdown of the rrp4 gene in early development using da-Gal4>UAS-rrp4 RI (da>rrp4 RI) or control RNAi (da> w RI). (C) Microphotographs of ey-Gal4-driven rrp4 RNAi flies with co-overexpression of WT and G30V hEXOSC2. Genotypes are ey-Gal4>UAS-rrp4 RNAi; UAS-hEXOSC2 (top) and ey-Gal4>UAS-rrp4 RNAi; UAS-hEXOSC2-G30 V (bottom). (D) Quantification of the eye size of flies shown in (C). ** indicates P < 0.01 in Student’s t test (n = 4). (E) Diagram of deletion alleles from CRISPR-mediated knockout of the fly rrp4 gene. Green labeled sequences are inserted fragment in mutant 48 line. (F) Information on the deleted or inserted nucleotides in the CRISPR lines, and summary of their genetic interaction with various rrp4 alleles. (G) Microphotographs of fly eyes containing eyFLP-generated homozygous clones of the rrp4 M13, M39 or M48 CRISPR knockout alleles. The genotypes are ey-Flp/+; FRT42D, rrp4 M13/FRT42D, w+, cl (rrp4 M13 clone), ey-Flp/+; FRT42D, rrp4 M39/FRT42D, w+, cl (rrp4 M39 clone), or ey-Flp/+; FRT42D, rrp4 M48/FRT42D, w+, cl (rrp4 M48 clone). cl stands for cell lethal.
