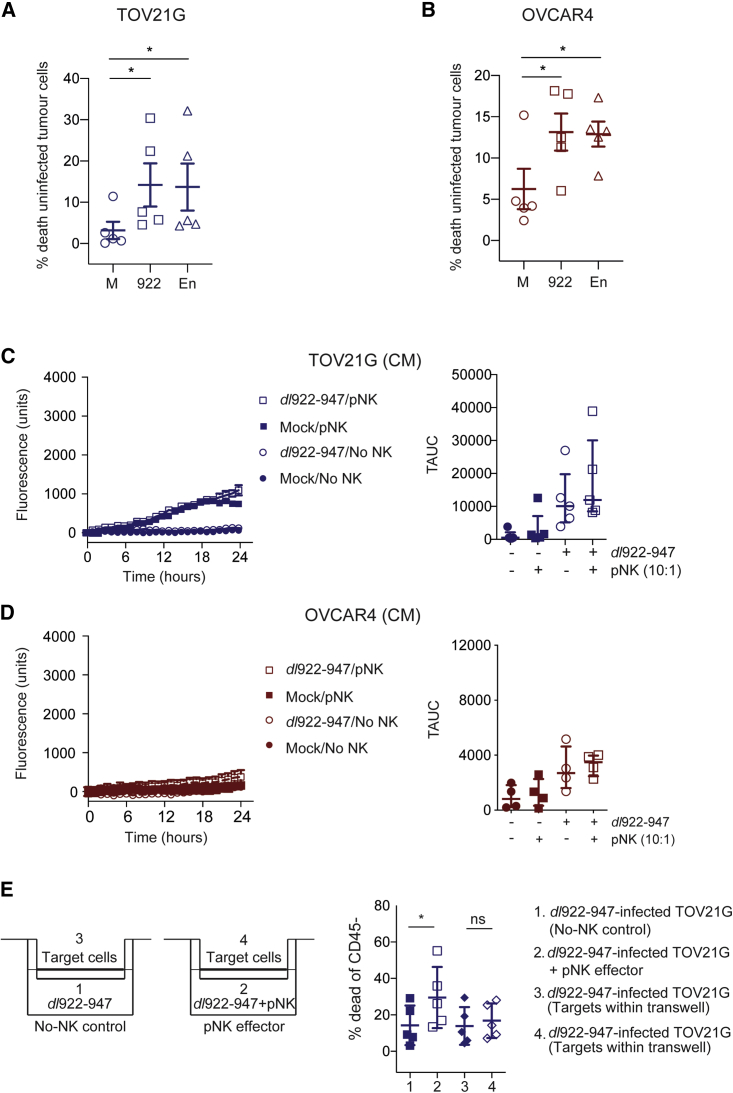
Figure 4.
Activated NK Augmented Killing of Uninfected Target Cells and Contact Dependence of NK Cytotoxicity
Cytotoxicity of activated peripheral blood NK cells (pNK) against cell-tracker marked and uninfected (A) TOV21G and (B) OVCAR4 was assessed by flow cytometry (n = 5 for each line; paired t tests). Cytotoxicity of pNK against uninfected (C) TOV21G (n = 5) and (D) OVCAR4 (n = 4) in the presence or absence of conditioned medium (CM) from dl922-947-infected TOV21G and OVCAR4, respectively. Cytotoxicity was assessed using live-cell imaging. Fluorescence counts over time from individual experiments (left) and summary data (right) are presented. (E) Target TOV21G were infected with dl922-947 (MOI 10, 48 h) in 12-well plates or in transwell inserts (group 1–4). Cell-free medium control (group 1) or pNK (group 2) were then incubated with virus-infected TOV21G for 18 h. Cell death of TOV21G in transwells (group 3 and 4), prevented from contact with NK cells but exposed to the environment of group 1 and 2, was compared by flow cytometry. The schematic representation of each group is shown on the left, with summary results (n = 5) on the right (paired t tests).