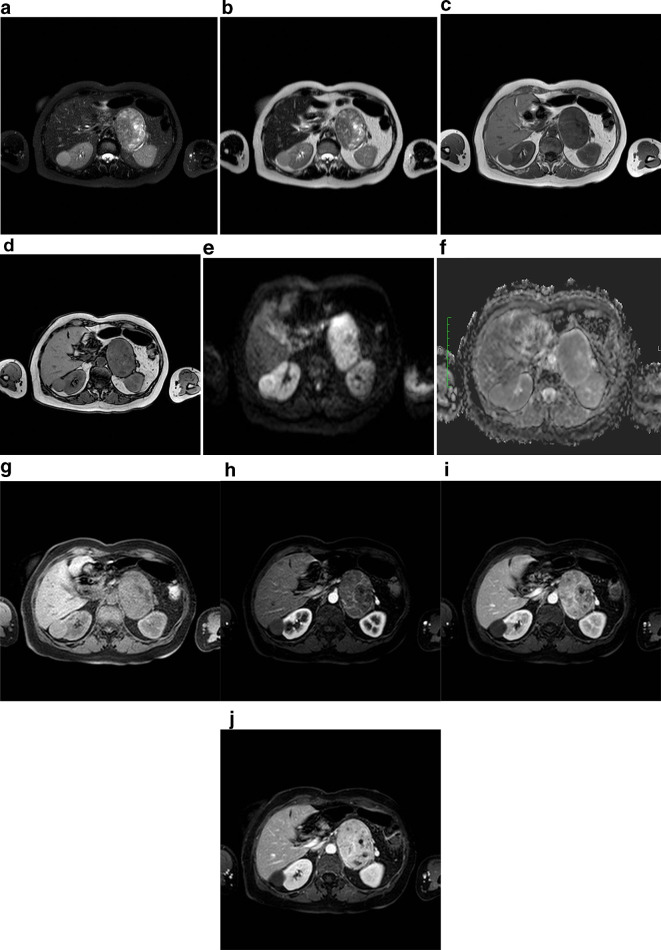
Figure 1. .
MRI examination of our patient, 61-years-old female, with left adrenal mass. (a) T2 (fat sat) weighted axial image shows voluminous and well-circumscribed solid mass in the left adrenal gland area, with heterogeneous high signal intensity, due to the presence of cystic components, also visible on (b) T2 weighted axial image. The lesion has well defined margins and fluid signal intensity areas; (c, d) T1 weighted images in phase and out of phase show the absence of signal intensity drop in opposed phase acquisitions, suggesting that intracellular fat was not present in the mass. Note also the regular profile and smooth margins of the mass; (e, f) DWI b 800 and relative ADC map axial image at the level of the adrenal mass show the presence of moderate diffusivity restriction due to lesion hypercellularity; (g) T1 (fat sat) weighted images before and (h, i, l) after paramagnetic contrast medium intravenous injection show clearly the progressive and heterogeneous contrast enhancement of the adrenal mass, with no evidence of adjacent structures infiltration. ADC, apparent diffusion coefficient; DWI, diffusion-weighted imaging.