Figure 1.
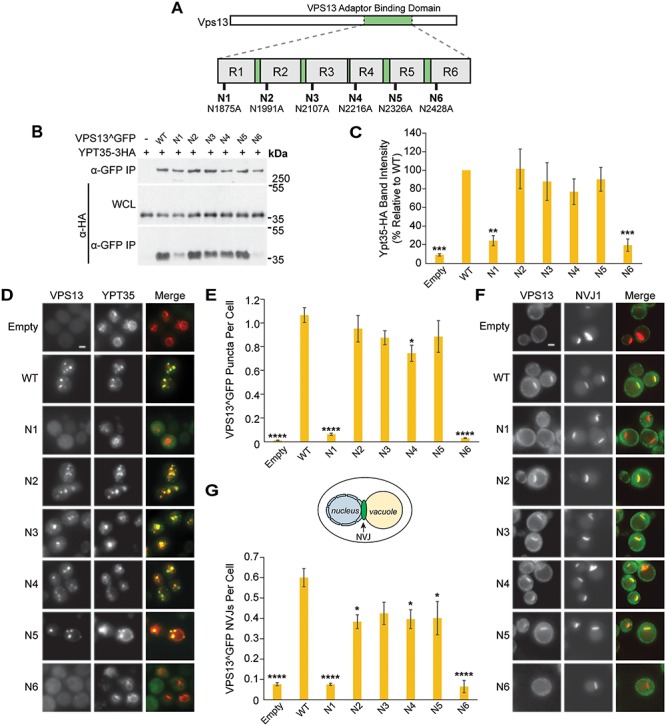
Mutations in the Vps13 VAB domain disrupt its interaction with the endosomal adaptor Ypt35. (A) Schematic of Vps13 VAB domain indicating the position of the mutated conserved asparagines in repeats 1–6 (R1–R6). (B) Co-IP of WT or mutant Vps13^GFP with Ypt35-3HA overexpressed from the ADH1 promoter. Proteins were expressed on plasmids in vps13Δ strains. WCL, whole-cell lysate. (C) Densitometry analysis of Ypt35-HA co-IP bands shown in (B); one-way ANOVA with Dunnett-corrected post hoc test; n = 4; ***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01. (D) Localization of WT or mutant Vps13^GFP to bright puncta colocalizing with ADH1pr-driven Ypt35-RFP. Proteins were expressed on plasmids in ypt35Δ strains. (E) Automated quantitation of Vps13^GFP puncta from (D). One-way ANOVA with Dunnett-corrected post hoc test; n = 3; cells/strain/replicate ≥1370; ****P < 0.0001; *P < 0.05. (F) Localization of WT or mutant Vps13^GFP to NVJ1-RFP-labeled NVJs in acetate-based media. Proteins were expressed on plasmids in vps13Δ strains. (G) Automated quantitation of the number of Vps13^GFP-labeled NVJs, from (F). The diagram shows the location of the NVJ. One-way ANOVA with Dunnett-corrected post hoc test; n = 3, cells/strain/replicate ≥495; ****P < 0.0001; *P < 0.05. Error bars indicate SEM. Bars, 2 μm.
