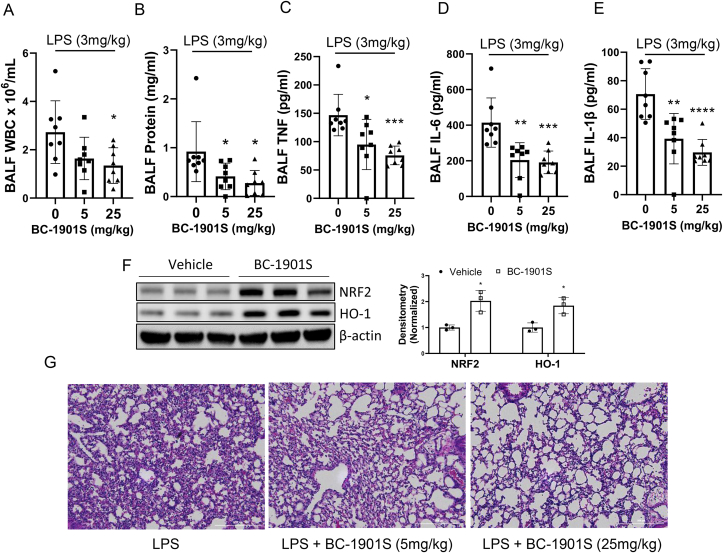
Fig. 4.
BC-1901S ameliorates LPS-induced pulmonary inflammation. C57BL/6J mice (n = 8 per group) were treated with intra-tracheal LPS (3 mg/kg) and either control (corn oil, i.p.) or BC-1901S at 5 mg/kg or 25 mg/kg (i.p.). 18h later, mice were euthanized and A) Broncho-alveolar lavage fluid (BALF) WBC count, B) BALF protein concentrations, C-E) BALF TNF, IL-6 and IL-1β were measured. Data represent mean ± SD. (F). Representative immunoblots and densitometry for NRF2, HO-1, and β-Actin from lung homogenates from LPS or LPS/BC-1901S (25 mg/kg) co-treated mice. Data represent mean ± SD. G) Representative lung histological images (H&E staining) from LPS and LPS/BC-1901S co-treated mice. P < 0.05, *; P < 0.01, **; P < 0.001, ***; P < 0.0001, ****; by one-way ANOVA with adjusted P-value for multiple comparisons (Dunnett's) compared to control or “0.”