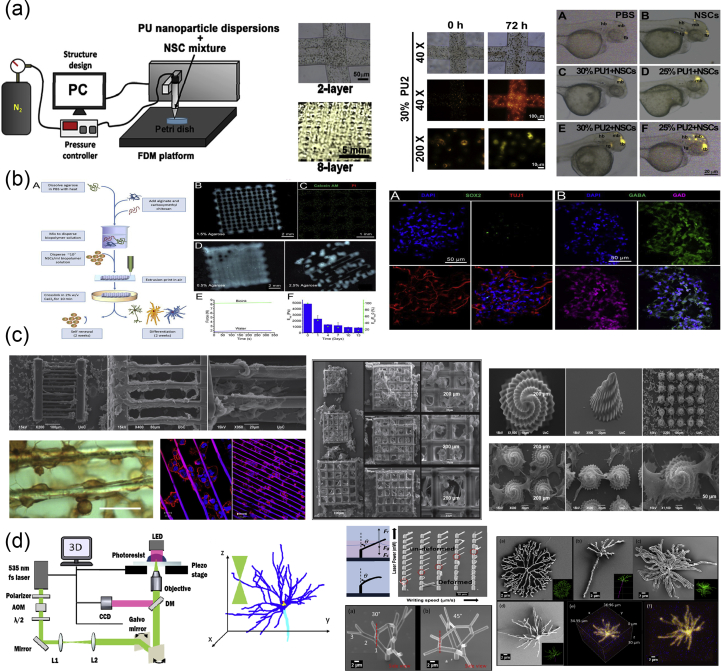
Fig. 14.
Three-dimensional printed scaffolds for CNS applications. (a) Use of FDM technique for bioprinting 3D scaffolds composed of PU and NSCs to support neural cell differentiation [179], (b) direct-write printing of bioink composed of hydrogel and hNSCs into porous 3D scaffolds to study human brain development and function [182], (c) PLA-based 3D structures written via DLW can be used as test bed for neural tissue engineering applications [183], and (d) zirconium-based 3D biomimetic neuron structures fabricated using the DLW method [184]. Images adapted with permission from (a) Hsieh et al. [179], (b) Gu et al. [182], (c) Melissinaki et al. [183], and (d) Yu et al. [184]. CNS, central nervous system; 3D, three-dimensional; DLW, direct laser writing; PU, polyurethane; NSC, neural stem cell; PLA, polylactic acid; hNSCs, human neural stem cells; FDM, fused deposition modeling; LED, light-emitting diode; CCD, charge-coupled device; DM, dichroic mirror; AOM, acousto-optic modulator.