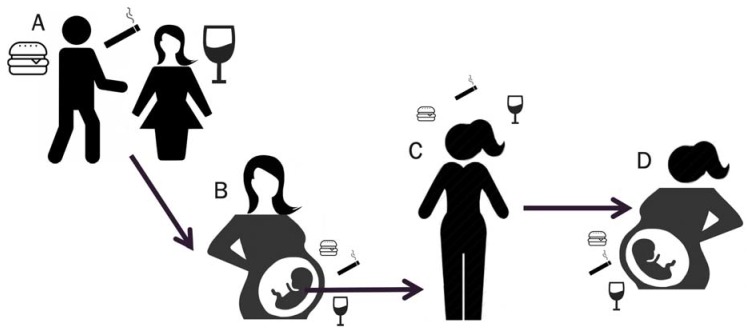
Figure 1.
Conceptual model for inherited epigenetic susceptibility to disease. Disease risk in a woman (C) may be affected by not only her own lifestyle and environmental exposures but also by what she was exposed to through her mother in utero (B) and even through both parents’ pre-conception via exposure-mediated epigenetic changes in their germ cells (A). Likewise, the woman’s exposures may affect her future child’s disease risk (D).