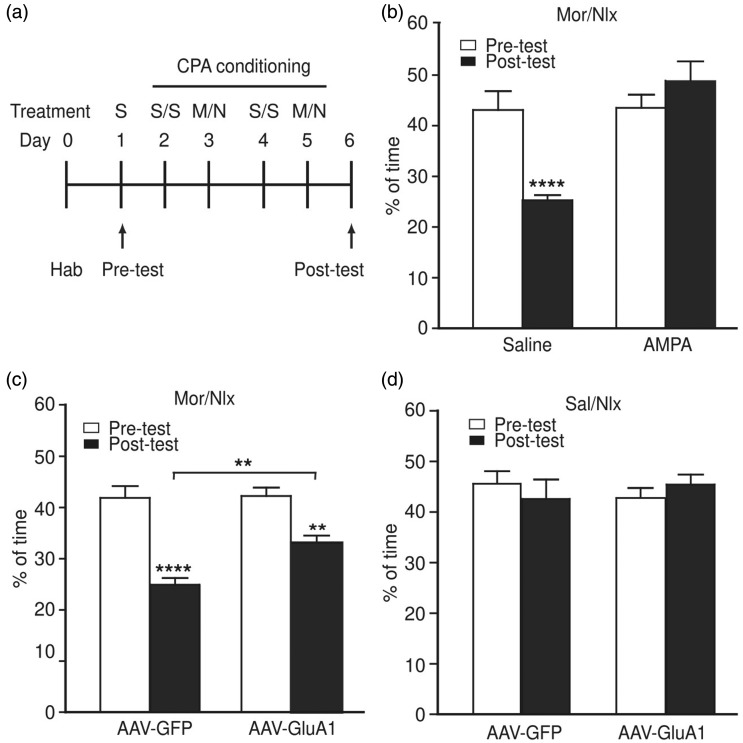
Figure 4.
Overexpression of GluA1 in central amygdala inhibits morphine withdrawal-induced aversion. (a) Schematic illustration of experimental procedures for induction of CPA by naloxone-precipitated morphine withdrawal. S, saline; M, morphine; N, naloxone; Hab, habituation. (b) CPA behavior in rats with naloxone (nlx)-precipitated morphine (mor) withdrawal after bilateral infusion of saline (n = 6 rats) or AMPA (100 ng each side, n = 8 rats) into CeA. (c, d) CPA behavior in rats with naloxone-precipitated morphine withdrawal (c, n = 9 rats each group) and in rats conditioned with saline (sal) and naloxone (d, n = 6 rats each group) after bilateral infusion of AAV-GFP or AAV-GluA1 into CeA. **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001 (two-way analysis of variance).
CPA: conditioned place aversion; AAV: adeno-associated virus; GFP: green fluorescent protein.