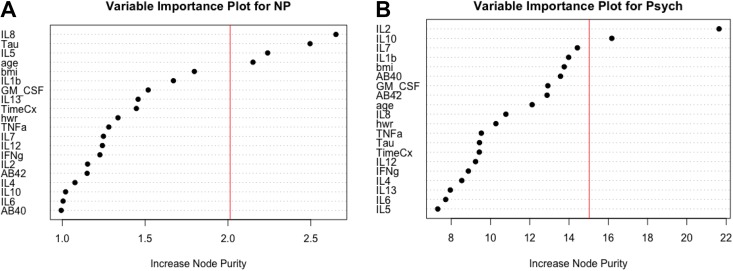
Figure 2.
(A) Variable importance plot of features in the random forest regression model with the neuropsychological (NP) composite score as the dependent variable. All the variables on the y-axis were included as features in the model. IL-8 (interleukin 8), tau, IL-5 (interleukin 5), and age were identified as the most important features, or predictors, in the model per the increase in node purity index. The vertical line represents the a priori threshold (1 SD above the mean) for determining the most important model features. Together, these features explain 71% of the variance in NP composite scores. (B) Variable importance plot of features in the random forest regression model with the psychosomatic (Psych) composite score as the dependent variable. All the variables on the y-axis were included as features in the model. IL-2 (interleukin 8) and IL-10 (interleukin 10) were identified as the most important features, or predictors, in the model per the increase in node purity index. The vertical line represents the a priori threshold (1 SD above the mean) for determining the most important model features. Together, these features explain 74% of the variance in Psych composite scores. AB = amyloid beta; BMI = body mass index; GM-CSF = granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; HWR = hip-to-waist ratio; IFNg = interferon gamma; IL = interleukin; IL12 = interleukin-12; TimeCx = time since chemotherapy; TNFa = tumor necrosis factor-alpha.