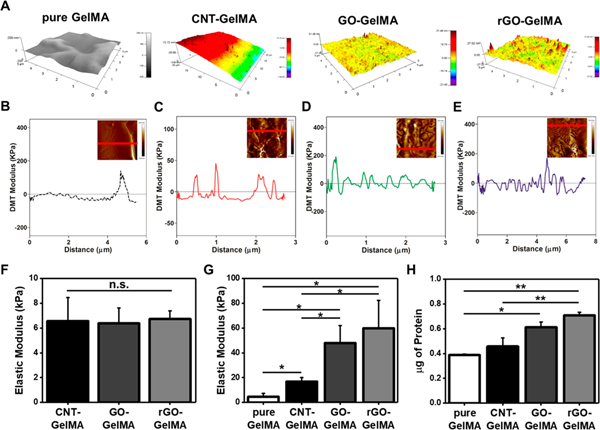
Figure 2.
Topological and mechanical characterizations of engineered hybrid hydrogels and protein adsorption onto their surface. (A) Spatial topography of pure, CNT-, GO-, and rGO-GelMA, measured by AFM. DMT modulus distribution profile of (B) pure, (C) CNT-, (d) GO-, and (E) rGO-GelMA along the specified line in inset AFM images of each condition. (F) Macroscale elastic modulus of CNT-, GO-, and rGO- GelMA (N = 4 for CNT, N =5 for GO, N = 4 for rGO). (G) Local elastic modulus of pure, CNT-, GO-, and rGO-GelMA obtained from the force—deformation plots in (B)-(E) (N = 3). (H) Quantification of absorbed proteins on the surface of pure, CNT-, GO-, and rGO-GelMA (N = 2) (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.005). Error bars represent standard deviation.