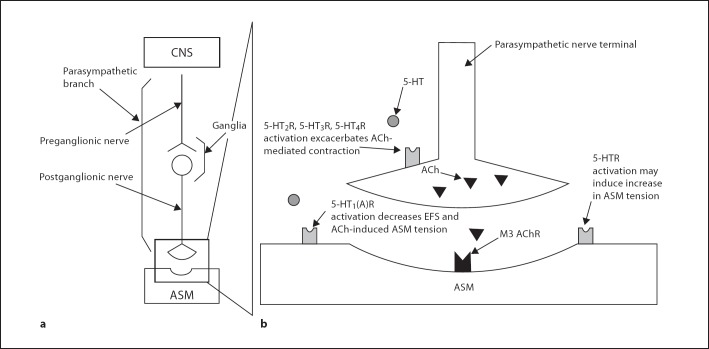
Fig. 10.
Working model of parasympathetic ASM control. a Parasympathetic signaling pathway from CNS to AMS. b Exploded view of parasympathetic nerve terminal and neuromuscular junction highlighting the proposed sites of 5-HT's modulation of ASM contraction. Activation of 5-HT receptors on cholinergic nerve terminal enhances ACh release during parasympathetic activation. A specific 5-HT1 receptor, possibly the 5-HT1A subtype, located on ASM, induces muscle relaxation when activated. There is some evidence that 5-HT receptors located directly on ASM may cause an increase in ASM activity when activated. 5-HTR = Serotonin receptor; M3 = muscarinic receptor.