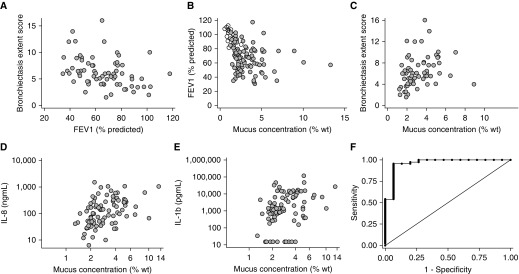
Figure 5.
Association between mucus percent solids and clinical outcomes in BLESS (Bronchiectasis and Low-Dose Erythromycin Study) subjects with non–cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis (NCFB). (A) The high-resolution chest computed tomography bronchiectasis extent score significantly correlated with FEV1 (Spearman rho [r] [95% confidence interval (CI)] = 0.40 [−0.61 to −0.19], P < 0.001). (B) FEV1 significantly correlated inversely with mucus percent solids (r [95% CI] = −0.22 [−0.43 to −0.01], P = 0.03), and (C) mucus concentration correlated positively with high-resolution chest computed tomography extent scores (r [95% CI] = 0.41 [0.19–0.63], P < 0.001). Mucus percent solids was significantly associated with the concentration of (D) IL-8 (r [95% CI] = 0.48 [0.32–0.64], P < 0.001) and (E) IL-1β (r [95% CI] = 0.40 [0.22–0.56], P < 0.001) in sputum. (F) Ability of mucus concentration (percent solids) to diagnose NCFB. Area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve = 0.9603. Area under the ROC curve for total mucins in NCFB versus control cohorts = 0.949 (see Figure E5). wt = weight.