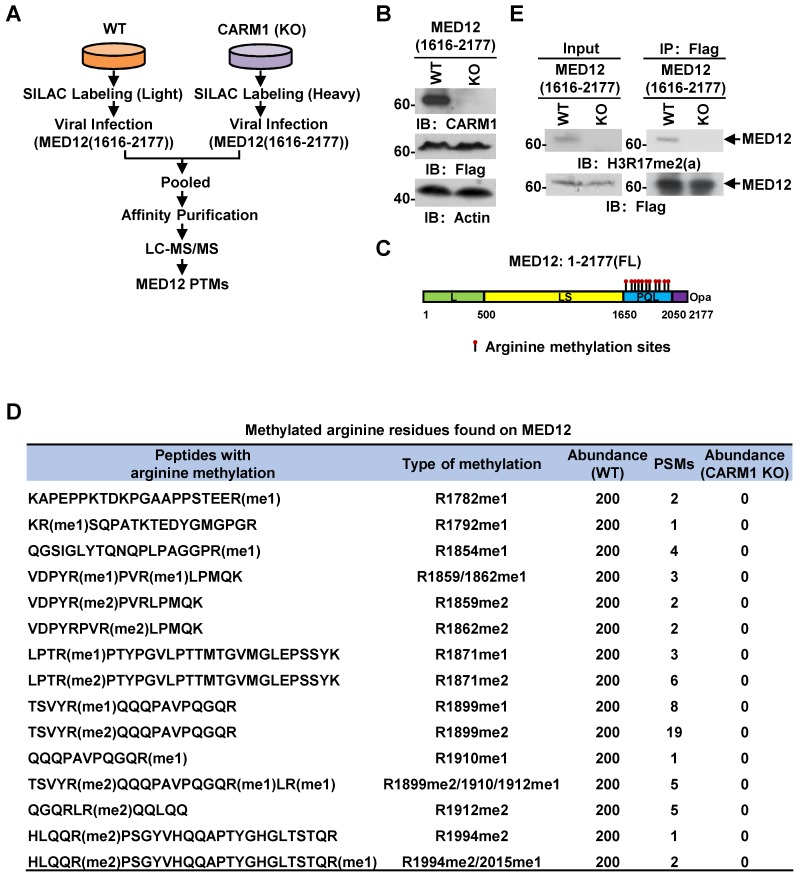
Figure 4.
MED12 is hypermethylated by CARM1. (A) Experimental flowchart for detecting post translational modifications (PTMs) of C-terminus of MED12 (1616-2177) in wild type (WT) or CARM1 knockout (KO) MCF7 cells. (B) Cell lysates as described in (A) were subjected to immunoblotting (IB) analysis with antibodies as indicated. Actin was served as a loading control. (C) Schematic representation of the domain architecture of MED12 protein. Leucine-rich (L) domain (light green); Leucine-serine-rich (LS) domain (yellow); Proline-glutamine-leucine (PQL) domain (light blue); Poly-glutamine (Opa) domain (purple). Arginine methylation sites identified in the PQL domain were shown by matchsticks. (D) Methylated arginine residues identified in the C-terminus of MED12 following the protocol as described in (A). me1: mono-methylation; me2: di-methylation. PSM: peptide spectrum match. (E) WT and CARM1 KO cells were infected with lenti-viral vectors expressing Flag-tagged MED12 C-terminus (1616-2177), lysed and subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-Flag antibody followed by immunoblotting (IB) analysis with antibodies as indicated. Anti-H3R17me2(a) antibody was used to detect methylated MED12.