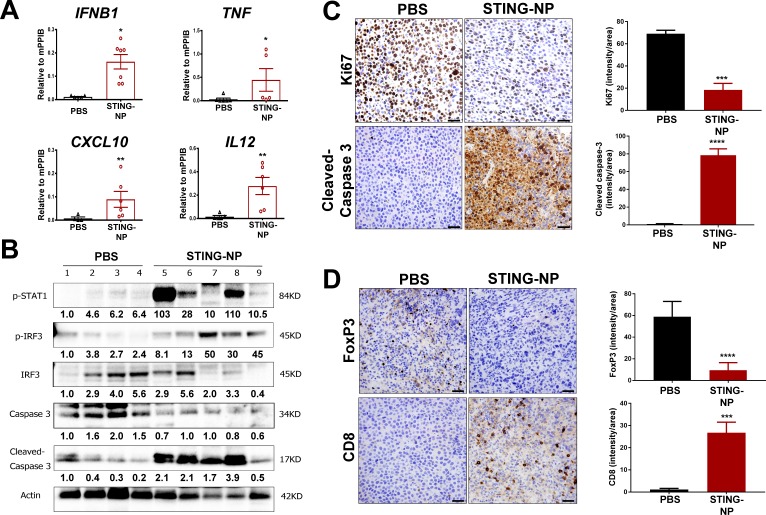
Figure 4.
STING activation in neuroblastoma generates an immunogenic, tumoricidal, and T-cell inflamed tumor microenvironment. Mice with 200 mm3 Neuro-2a tumors were administered PBS or STING-NPs (10 µg cGAMP) intratumorally three times, spaced 3 days apart, and tumors were harvested 48 hours following the last treatment. (A) qRT-PCR analysis of IFNB1, TNF, CXCL10, and IL12 gene expression in injected Neuro-2a tumors. n=5 to 7 mice per group represented as mean±SEM, *p<0.05, **p<0.01 indicate a statistically significant difference using a two-tailed Mann-Whitney U test. (B) Neuro-2a tumor lysates (n=4–5) were analyzed using western blot for phospho-STAT1 (p-STAT1), IRF3, and phospho-IRF3 (p-IRF3), caspase 3, and cleaved caspase 3. Gel loading was normalized for equal actin. The density of bands is shown under each immunoblot, after normalization to the levels of actin. (C/D) Immunohistochemical staining of tumor sections for cleaved caspase-3 (apoptosis), Ki-67 (proliferation), CD8, and FoxP3 and corresponding quantification of staining intensity using ImageJ software. Data shown as mean±SD for n=3 Neuro-2a tumors, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001 indicate a statistically significant difference using a Student’s t-test. cGAMP, cyclic guanosine monophosphate–adenosine monophosphate; qRT-PCR, quantitative real-time PCR; STING, stimulator of interferon genes; STING-NPs, STING-activating nanoparticles.