Figure 2.
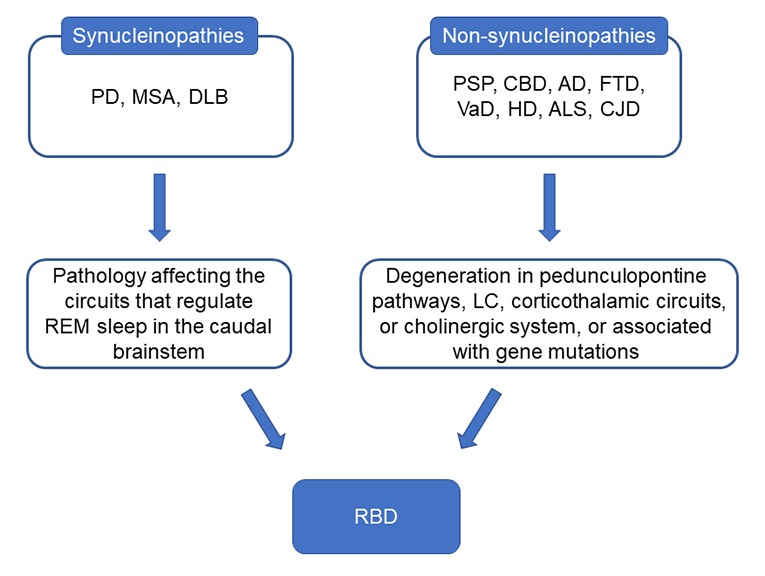
The possible mechanisms of RBD associated with synucleinopathies or non-synucleinopathies. Lesions in caudal brainstem are thought to eliminate atonia during REM sleep and the brainstem is the same structure where α-syn pathology might begin in synucleinopathies. In non-synucleinopatheis, the pathological changes may affect pedunculopontine pathways, locus coeruleus (LC), corticothalamic circuits or cholinergic system and finally affect the REM sleep regulating systems to induce RBD.
